Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-3C is targeted to and regulates expression from the bidirectional LMP-1/2B promoter
- PMID: 16956945
- PMCID: PMC1642179
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00897-06
Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-3C is targeted to and regulates expression from the bidirectional LMP-1/2B promoter
Abstract
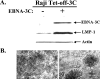
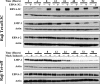
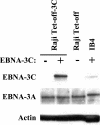
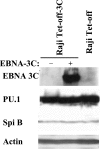
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 3C (EBNA-3C) is essential for EBV-mediated immortalization of human B lymphocytes and regulates both the cell cycle and transcription. Transient reporter gene assays have implicated a pivotal role for EBNA-3C in the regulation of transcription of the majority of latency-associated genes expressed during the EBV growth program, including the viral oncoprotein LMP-1. To examine the regulation of latency gene expression by EBNA-3C, we generated an EBV-positive cell line that inducibly expresses EBNA-3C. This cell line allowed us to examine expression from the endogenous latency gene promoters in the context of an actual latent infection and the presence of other EBNA proteins, in particular EBNA-2, which is presumed to coregulate transcription with EBNA-3C. EBNA-3C induced the expression of both LMP-1 and LMP-2B mRNAs from the bidirectional LMP-1/LMP-2B promoter. In contrast, no effect was seen on expression from the common EBNA promoter Cp, which is responsive to EBNA-3C in reporter assays. Activation of LMP expression was not the consequence of increases in EBNA-2, PU.1 or Spi-B transcription factors, all of which are believed to be critical for activation of LMP-1. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays furthermore indicated that EBNA-3C is present at the bidirectional LMP-1/LMP-2B promoter. These results indicate that EBNA-3C directly activates the expression of LMP-1 and LMP-2B but is unlikely to significantly regulate EBNA expression via Cp under normal growth conditions.
Figures


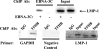
Similar articles
-
Epstein-barr virus nuclear antigen 3C activates the latent membrane protein 1 promoter in the presence of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 through sequences encompassing an spi-1/Spi-B binding site.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(11):5151-60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.11.5151-5160.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10799590 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-binding studies of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA-2): evidence for complex formation by latent membrane protein gene promoter-binding proteins in EBNA-2-positive cell lines.J Gen Virol. 1994 Nov;75 ( Pt 11):3067-79. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-11-3067. J Gen Virol. 1994. PMID: 7964616
-
EBNA-2 upregulation of Epstein-Barr virus latency promoters and the cellular CD23 promoter utilizes a common targeting intermediate, CBF1.J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5375-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.9.5375-5383.1994. J Virol. 1994. PMID: 8057421 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine mediated induction of the major Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded transforming protein, LMP-1.Immunol Lett. 2006 Apr 15;104(1-2):83-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2005.11.003. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Immunol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16386314 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent genes.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jan 23;47(1):e131. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.84. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25613728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of integrin receptor-signaling genes by Epstein-Barr virus EBNA 3C via promoter-proximal and -distal binding elements.J Virol. 2012 May;86(9):5165-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07161-11. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22357270 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of CTCF and DNA methyltransferases DNMT1 and DNMT3B to Epstein-Barr virus restricted latency.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(2):1034-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05923-11. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22072770 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression patterns of EBV infected EBNA-3A positive and negative human B lymphocytes.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Jul;5(7):e1000506. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000506. Epub 2009 Jul 3. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19578441 Free PMC article.
-
c-Myc Represses Transcription of Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 Early after Primary B Cell Infection.J Virol. 2018 Jan 2;92(2):e01178-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01178-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29118124 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein EBNA3C residues critical for maintaining lymphoblastoid cell growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 17;106(11):4419-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813134106. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19237563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allday, M. J., D. H. Crawford, and J. A. Thomas. 1993. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 6 induces expression of the EBV latent membrane protein and an activated phenotype in Raji cells. J. Gen. Virol. 74:361-369. - PubMed
-
- Boos, H., R. Berger, C. Kuklik-Roos, T. Iftner, and N. Mueller-Lantzsch. 1987. Enhancement of Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP) expression by serum, TPA, or n-butyrate in latently infected Raji cells. Virology 159:161-165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

