The role of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 in pathogenesis of sporadic Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 16957079
- PMCID: PMC6674490
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0341-06.2006
The role of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 in pathogenesis of sporadic Parkinson's disease
Abstract
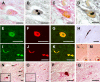
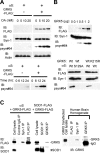
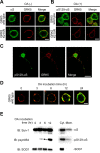
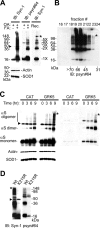
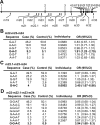
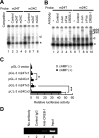
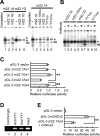
Sporadic Parkinson's disease (sPD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by selective degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Although the pathogenesis of the disease remains undetermined, phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein and its oligomer formation seem to play a key role. However, the protein kinase(s) involved in the phosphorylation in the pathogenesis of sPD has not been identified. Here, we found that G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5) accumulated in Lewy bodies and colocalized with alpha-synuclein in the pathological structures of the brains of sPD patients. In cotransfected cells, GRK5 phosphorylated Ser-129 of alpha-synuclein at the plasma membrane and induced translocation of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein to the perikaryal area. GRK5-catalyzed phosphorylation also promoted the formation of soluble oligomers and aggregates of alpha-synuclein. Genetic association study revealed haplotypic association of the GRK5 gene with susceptibility to sPD. The haplotype contained two functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms, m22.1 and m24, in introns of the GRK5 gene, which bound to YY1 (Yin Yang-1) and CREB-1 (cAMP response element-binding protein 1), respectively, and increased transcriptional activity of the reporter gene. The results suggest that phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein by GRK5 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of sPD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of G-protein coupled receptor kinase 2 in paired helical filaments and neurofibrillary tangles.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006 Dec;65(12):1157-69. doi: 10.1097/01.jnen.0000248542.82681.12. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 17146290
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5, overexpressed in the alpha-synuclein up-regulation model of Parkinson's disease, regulates bcl-2 expression.Brain Res. 2010 Jan 11;1307:134-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.10.036. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 19852948
-
In vivo modulation of polo-like kinases supports a key role for PLK2 in Ser129 α-synuclein phosphorylation in mouse brain.Neuroscience. 2014 Jan 3;256:72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.061. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24128992
-
α-Synuclein phosphorylation as a therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease.Rev Neurosci. 2012 Mar 21;23(2):191-8. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2011-0067. Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22499677 Review.
-
Parkinson's disease and alpha synuclein: is Parkinson's disease a prion-like disorder?Mov Disord. 2013 Jan;28(1):31-40. doi: 10.1002/mds.25373. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 23390095 Review.
Cited by
-
Posttranslational Modifications and Clearing of α-Synuclein Aggregates in Yeast.Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 23;5(2):617-34. doi: 10.3390/biom5020617. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 25915624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Doublecortin-like Kinase 1 Regulates α-Synuclein Levels and Toxicity.J Neurosci. 2020 Jan 8;40(2):459-477. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1076-19.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 20. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31748376 Free PMC article.
-
GRK5 Is Associated with the Regulation of Methadone Dosage in Heroin Dependence.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 Oct 1;21(10):910-917. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy066. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30060048 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Serine 129 Phosphorylation on α-Synuclein Aggregation, Membrane Association, and Internalization.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 26;291(9):4374-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.705095. Epub 2015 Dec 30. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26719332 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinases in neurodegenerative diseases: current understandings and implications for drug discovery.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 May 7;10(1):146. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02179-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40328798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arawaka S, Hasegawa H, Tandon A, Janus C, Chen F, Yu G, Kikuchi K, Koyama S, Kato T, Fraser PE, St George-Hyslop P. The levels of mature glycosylated nicastrin are regulated and correlate with gamma-secretase processing of amyloid beta-precursor protein. J Neurochem. 2002;83:1065–1071. - PubMed
-
- Bucciantini M, Giannoni E, Chiti F, Baroni F, Formigli L, Zurdo J, Taddei N, Ramponi G, Dobson CM, Stefani M. Inherent toxicity of aggregates implies a common mechanism for protein misfolding diseases. Nature. 2002;416:507–511. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Feany MB. Alpha-synuclein phosphorylation controls neurotoxicity and inclusion formation in a Drosophila model of Parkinson disease. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:657–663. - PubMed
-
- Chung KK, Dawson VL, Dawson TM. New insights into Parkinson's disease. J Neurol. 2003;250([Suppl 3]):III15–III24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
