Effects of the angiotensin II receptor blockers telmisartan vs valsartan in combination with hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg once daily for the treatment of hypertension
- PMID: 16957424
- PMCID: PMC8109706
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2006.05411.x
Effects of the angiotensin II receptor blockers telmisartan vs valsartan in combination with hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg once daily for the treatment of hypertension
Abstract
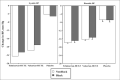
To attain recent goals of blood pressure (BP) control, multiple drug therapy combinations are required, including higher doses of thiazide diuretics in combination with other classes of antihypertensive drug therapy. Thus, the authors evaluated the antihypertensive effects of telmisartan vs valsartan when combined with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 25 mg in a large (N=1066), placebo-controlled trial in patients with stage 1 or 2 hypertension. The primary end points were the changes from baseline in seated diastolic and systolic BP at the end of the 8-week treatment period. Safety end points included adverse events, changes in laboratory parameters, and pulse rate. Changes from baseline in BP following telmisartan-HCTZ (-24.0/-17.6 mm Hg) were significantly greater than both placebo (-4.4/-6.8 mm Hg) and valsartan-HCTZ (-21.2/-16.1 mm Hg) (vs placebo, P<.001 for systolic and diastolic BP; vs valsartan-HCTZ, P=.004 for systolic BP and P=.019 for diastolic BP). The total number of patients with at least 1 adverse event reported were similar among the 3 treatment groups (placebo, 49%; telmisartan-HCTZ, 43%; and valsartan-HCTZ, 38%). In conclusion, telmisartan-HCTZ at doses of 80/25 mg lowered both systolic and diastolic BP to a greater extent than valsartan-HCTZ at doses of 160/25 mg. These data support using a higher dose of a thiazide diuretic (25 mg) with a long-acting angiotensin receptor blocker as a useful strategy for improving hypertension control.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide versus valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide in obese hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes: the SMOOTH study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007 Oct 2;6:28. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-6-28. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007. PMID: 17910747 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of angiotensin receptor blockade in combination with hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg in 2121 patients with stage 1-2 hypertension.J Hum Hypertens. 2009 Dec;23(12):817-25. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2009.28. Epub 2009 Apr 9. J Hum Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19357698 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of the angiotensin II receptor blockers telmisartan versus valsartan in combination with hydrochlorothiazide: a large, confirmatory trial.Blood Press Monit. 2008 Feb;13(1):21-7. doi: 10.1097/MBP.0b013e3282f3859d. Blood Press Monit. 2008. PMID: 18199920 Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of telmisartan versus valsartan in the management of essential hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2010 Jun;12(6):414-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2010.00287.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2010. PMID: 20591086 Free PMC article.
-
A review of telmisartan in the treatment of hypertension: blood pressure control in the early morning hours.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006;2(3):195-201. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.3.195. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006. PMID: 17326326 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the benefits of early treatment initiation with single-pill combinations of telmisartan with amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013;9:521-8. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S48291. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013. PMID: 24082785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Results of an olmesartan medoxomil-based treatment regimen in hypertensive patients.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2008 Dec;10(12):911-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.00045.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2008. PMID: 19120717 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Results of increasing doses of hydrochlorothiazide in combination with an angiotensin receptor blocker in patients with uncontrolled hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2008 Aug;10(8):612-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.08187.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2008. PMID: 18772643 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Telmisartan with Hydrochlorothiazide versus Valsartan with Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Hypertension.Int J Hypertens. 2012;2012:976828. doi: 10.1155/2012/976828. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Int J Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22844584 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide versus valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide in obese hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes: the SMOOTH study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007 Oct 2;6:28. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-6-28. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007. PMID: 17910747 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, et al, for the Prospective Studies Collaboration . Age‐specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta‐analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360:1903–;1913. - PubMed
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, et al. Effects of intensive blood‐pressure lowering and low‐dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomized trial. Lancet. 1998;351:1755–;1762. - PubMed
-
- The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–;2572. - PubMed
-
- European Society of Hypertension‐European Society of Cardiology. 2003. European Society of Hypertension‐European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 2003;21:1011–;1054. - PubMed
-
- Ruddy MC, Kostis JB. Angiotensin receptor antagonists. In: Oparil S, Weber MA, eds. Hypertension. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Co; 2000:621–;637.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

