LR11/SorLA expression is reduced in sporadic Alzheimer disease but not in familial Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 16957580
- PMCID: PMC2663339
- DOI: 10.1097/01.jnen.0000228205.19915.20
LR11/SorLA expression is reduced in sporadic Alzheimer disease but not in familial Alzheimer disease
Abstract
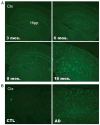
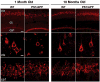
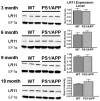
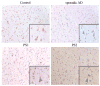
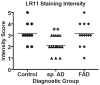
LR11 is an ApoE receptor that is enriched in the brain. We have shown that LR11 is markedly downregulated in patients with sporadic Alzheimer disease (AD). This finding led us to explore whether reduced LR11 expression reflects a primary mechanism of disease or merely a secondary consequence of other AD-associated changes. Therefore, LR11 expression was assessed in a transgenic mouse model of AD and familial AD (FAD) brains. Immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting of LR11 in PS1/APP transgenic and wild-type mice indicated that LR11 levels are not affected by genotype or accumulation of amyloid pathology. LR11 expression was also evaluated based on immunoblotting and LR11 immunostaining intensity in human frontal cortex in controls, sporadic AD, and FAD, including cases with presenilin-1 (PS1) and presenilin-2 (PS2) mutations. Although LR11 was reduced in sporadic AD, there was no difference in protein level or staining intensity between control and FAD cases. The finding that LR11 expression is unaffected in both a mouse model of AD and autosomal-dominant forms of AD suggests that LR11 is not regulated by amyloid accumulation or other AD neuropathologic changes. We hypothesize that LR11 loss may be specific to sporadic AD and influence amyloid pathology through mechanisms independent of substrate-enzyme interactions regulated by FAD mutations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid increases SorLA/LR11, a sorting protein with reduced expression in sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD): relevance to AD prevention.J Neurosci. 2007 Dec 26;27(52):14299-307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3593-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18160637 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of LR11/SORLA enhances early pathology in a mouse model of amyloidosis: evidence for a proximal role in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 26;28(48):12877-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4582-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19036982 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of apolipoprotein E receptor LR11 in Alzheimer disease.Arch Neurol. 2004 Aug;61(8):1200-5. doi: 10.1001/archneur.61.8.1200. Arch Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15313836
-
sorLA: sorting out APP.Mol Interv. 2006 Apr;6(2):74-6, 58. doi: 10.1124/mi.6.2.4. Mol Interv. 2006. PMID: 16565469 Review.
-
Exploring the etiology of Alzheimer disease using molecular genetics.JAMA. 1997 Mar 12;277(10):825-31. JAMA. 1997. PMID: 9052714 Review.
Cited by
-
Sorting Out the Role of the Sortilin-Related Receptor 1 in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2020 May 2;4(1):123-140. doi: 10.3233/ADR-200177. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2020. PMID: 32587946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candidate-based screening via gene modulation in human neurons and astrocytes implicates FERMT2 in Aβ and TAU proteostasis.Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Mar 1;28(5):718-735. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy376. Hum Mol Genet. 2019. PMID: 30371777 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative modelling of amyloidogenic processing and its influence by SORLA in Alzheimer's disease.EMBO J. 2012 Jan 4;31(1):187-200. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.352. Epub 2011 Oct 11. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 21989385 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Retromer Function in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease Is Dependent on Intracellular Cholesterol Accumulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 9;22(24):13256. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413256. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948052 Free PMC article.
-
The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease.Nat Genet. 2007 Feb;39(2):168-77. doi: 10.1038/ng1943. Epub 2007 Jan 14. Nat Genet. 2007. PMID: 17220890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:741–66. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer disease: Mechanistic understanding predicts novel therapies. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:627–38. - PubMed
-
- Sherrington R, Rogaev E, Liang Y, et al. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1995;375:754–60. - PubMed
-
- Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M, et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1991;349:704–706. - PubMed
-
- Murrell J, Farlow M, Ghetti B, et al. A mutation in the amyloid precursor protein associated with hereditary Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 1991;254:97–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

