Exploring the limits of RF shimming for high-field MRI of the human head
- PMID: 16958070
- PMCID: PMC4040521
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.21013
Exploring the limits of RF shimming for high-field MRI of the human head
Abstract
Several methods have been proposed for overcoming the effects of radiofrequency (RF) magnetic field inhomogeneity in high-field MRI. Some of these methods rely at least in part on the ability to independently control magnitude and phase of different drives in either one multielement RF coil or in different RF coils in a transmit array. The adjustment of these drive magnitudes and phases alone to create uniform RF magnetic (B(1)) fields has been called RF shimming, and has certain limits at every frequency as dictated by possible solutions to Maxwell's equations. Here we use numerical calculations to explore the limits of RF shimming in the human head. We found that a 16-element array can effectively shim a single slice at frequencies up to 600 MHz and the whole brain at up to 300 MHz, while an 80-element array can shim the whole brain at up to 600 MHz.
Figures

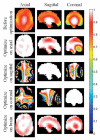
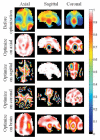
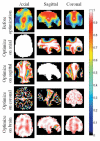
References
-
- Zhu Y, Watkins R, Giaquinto R, Hardy C, Kenwood G, Mathias S, Valent T, Denzin M, Hopkins J, Peterson W, Mock B. Parallel excitation on an eight transmit-channel MRI system. Proceedings of the 13th Annual Meeting of the ISMRM; Miami Beach, FL, USA. 2005. p. 14.
-
- Ullmann P, Junge S, Wick M, Ruhm W, Hennig J. Experimental verification of transmit SENSE with simultaneous RF-transmission on multiple channels. Proceedings of the 13th Annual Meeting of the ISMRM; Miami Beach, FL, USA. 2005. p. 15.
-
- Kurpad KN, Boskamp EB, Wright SM. A parallel transmit volume coil with independent control of currents on the array elements. Proceedings of the 13th Annual Meeting of the ISMRM; Miami Beach, FL, USA. 2005. p. 16.
-
- Hoult DI, Kolansky G, Kripiakevich D, King SB. The NMR multi-transmit phased array: a Cartesian feedback approach. J Magn Reson. 2004;171:64–70. - PubMed
-
- Adriany G, Van de Moortele PF, Wiesinger F, Moeller S, Strupp JP, Andersen P, Snyder C, Zhang X, Chen W, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P, Vaughan T, Ugurbil K. Transmit and receive transmission line arrays for 7 Tesla parallel imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2005;53:434–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

