The bacterial cytoskeleton
- PMID: 16959967
- PMCID: PMC1594594
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00017-06
The bacterial cytoskeleton
Abstract
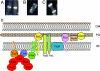
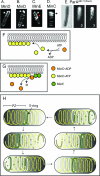
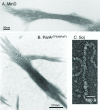
In recent years it has been shown that bacteria contain a number of cytoskeletal structures. The bacterial cytoplasmic elements include homologs of the three major types of eukaryotic cytoskeletal proteins (actin, tubulin, and intermediate filament proteins) and a fourth group, the MinD-ParA group, that appears to be unique to bacteria. The cytoskeletal structures play important roles in cell division, cell polarity, cell shape regulation, plasmid partition, and other functions. The proteins self-assemble into filamentous structures in vitro and form intracellular ordered structures in vivo. In addition, there are a number of filamentous bacterial elements that may turn out to be cytoskeletal in nature. This review attempts to summarize and integrate the in vivo and in vitro aspects of these systems and to evaluate the probable future directions of this active research field.
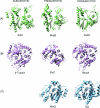
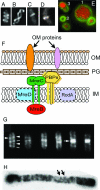
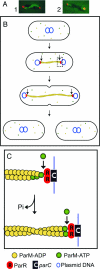
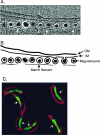
Figures
References
-
- Adachi, S., K. Hori, and S. Hiraga. 2006. Subcellular positioning of F plasmid mediated by dynamic localization of SopA and SopB. J. Mol. Biol. 356:850-863. - PubMed
-
- Alberts, B., A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts, and P. Walter. 2002. Molecular biology of the cell, 4th ed. Garland Science, New York, N.Y.
-
- Aldridge, C., J. Maple, and S. Moller. 2005. The molecular biology of plastid division in higher plants. J. Exp. Bot. 56:1061-1077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

