Development and validation of a fourfold multiplexed opsonization assay (MOPA4) for pneumococcal antibodies
- PMID: 16960111
- PMCID: PMC1563573
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00112-06
Development and validation of a fourfold multiplexed opsonization assay (MOPA4) for pneumococcal antibodies
Abstract
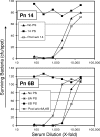
Opsonophagocytic killing assays (OPAs) are essential for developing and improving pneumococcal vaccines. There is a need for a high-throughput, reliable, standardized, and fully characterized OPA for pneumococcal antibodies. To meet the need, we have developed and characterized a fourfold multiplexed OPA (MOPA4) against 13 serotypes (1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F, and 23F) of pneumococci. Thirteen target bacteria were made resistant to only one of the following antibiotics: optochin, streptomycin, spectinomycin, and trimethoprim. Following optimization of assay conditions, accuracy of MOPA4 was determined by testing 30 sera from old adults in the MOPA4 and the single-serotype assays. The opsonization titers obtained with both assays agreed well (r(2) > 0.95). Although 22 (out of 390; approximately 6%) results differed more than twofold, the differences were not reproducible. The assay was specific: preabsorbing test sera with homologous polysaccharide (PS) completely abrogated opsonic activity, but a pool of unrelated PS (5 mug/ml of each) had no effect. Intra- and interassay coefficients of variation were 10 and 22%, respectively. MOPA4 results were unaffected by having different target pneumococcal serotypes in each assay group. Also, HL60 cell-to-bacteria ratios could be varied twofold without affecting the results. We conclude that MOPA4 is sensitive, accurate, specific, precise, and robust enough for large-scale clinical studies. Furthermore, MOPA4 should allow evaluation of multivalent pneumococcal vaccines with the limited volume of serum typically available from young children.
Figures

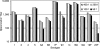
References
-
- Bogaert, D., M. Sluijter, R. De Groot, and P. W. Hermans. 2004. Multiplex opsonophagocytosis assay (MOPA): a useful tool for the monitoring of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Vaccine 22:4014-4020. - PubMed
-
- Fedson, D. S., and D. M. Musher. 1994. Pneumococcal vaccine, p. 517-564. In S. A. Plotkin and E. A. Mortimer (ed.), Vaccines, 2nd ed. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, Pa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

