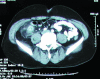
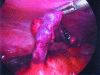
Acute appendicitis
- PMID: 16960208
- PMCID: PMC1562475
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.38940.664363.AE
Acute appendicitis
Figures
Comment in
-
Acute appendicitis: weighing up risks and benefits of investigations and treatments.BMJ. 2006 Sep 23;333(7569):652-3. doi: 10.1136/bmj.333.7569.652-b. BMJ. 2006. PMID: 16990328 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acute appendicitis: leaving normal looking appendices.BMJ. 2006 Sep 23;333(7569):652. doi: 10.1136/bmj.333.7569.652-a. BMJ. 2006. PMID: 16990329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acute appendicitis: acute appendicitis or acute appendicectomy?BMJ. 2006 Sep 23;333(7569):653. doi: 10.1136/bmj.333.7569.653. BMJ. 2006. PMID: 16990333 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Larner AJ. The aetiology of appendicitis. Br J Hosp Med 1988;39: 540-2. - PubMed
-
- Hospital Episode Statistics. Primary diagnosis: summary. www.hesonline.nhs.uk/Ease/servlet/ContentServer?siteID=1937&categoryID=202 (accessed 28 Aug 2006).
-
- Addiss DG, Shaffer N, Fowler BS, Tauxe RV. The epidemiology of appendicitis and appendectomy in the United States. Am J Epidemiol 1990;132: 910-25. - PubMed
-
- Murphy J. Two thousand operations for appendicitis, with deductions from his personal experience. Am J Med Sci 1904;128: 187-211.
-
- Andersson R. Meta-analysis of the clinical and laboratory diagnosis of appendicitis. Br J Surg 2004;91: 28-37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical