Familial chilblain lupus, a monogenic form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus, maps to chromosome 3p
- PMID: 16960810
- PMCID: PMC1592563
- DOI: 10.1086/507848
Familial chilblain lupus, a monogenic form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus, maps to chromosome 3p
Abstract
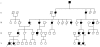
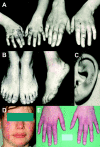
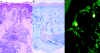
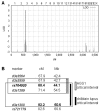
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a prototypic autoimmune disease. Apart from rare monogenic deficiencies of complement factors, where lupuslike disease may occur in association with other autoimmune diseases or high susceptibility to bacterial infections, its etiology is multifactorial in nature. Cutaneous findings are a hallmark of the disease and manifest either alone or in association with internal-organ disease. We describe a novel genodermatosis characterized by painful bluish-red inflammatory papular or nodular lesions in acral locations such as fingers, toes, nose, cheeks, and ears. The lesions sometimes appear plaquelike and tend to ulcerate. Manifestation usually begins in early childhood and is precipitated by cold and wet exposure. Apart from arthralgias, there is no evidence for internal-organ disease or an increased susceptibility to infection. Histological findings include a deep inflammatory infiltrate with perivascular distribution and granular deposits of immunoglobulins and complement along the basement membrane. Some affected individuals show antinuclear antibodies or immune complex formation, whereas cryoglobulins or cold agglutinins are absent. Thus, the findings are consistent with chilblain lupus, a rare form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Investigation of a large German kindred with 18 affected members suggests a highly penetrant trait with autosomal dominant inheritance. By single-nucleotide-polymorphism-based genomewide linkage analysis, the locus was mapped to chromosome 3p. Haplotype analysis defined the locus to a 13.8-cM interval with a LOD score of 5.04. This is the first description of a monogenic form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Identification of the gene responsible for familial chilblain lupus may shed light on the pathogenesis of common forms of connective-tissue disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
References
Web Resources
-
- ENSEMBL genome browser, http://www.ensembl.org/homo_sapiens/index.html
-
- GeneCards, http://www.genecards.org/index.shtml
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=OMIM
References
-
- Sontheimer RD (1997) The lexicon of cutaneous lupus erythematosus—a review and personal perspective on the nomenclature and classification of the cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus. Lupus 6:84–95 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

