Anomalous trichromats' judgments of surface color in natural scenes under different daylights
- PMID: 16962006
- PMCID: PMC1866190
- DOI: 10.1017/S0952523806233297
Anomalous trichromats' judgments of surface color in natural scenes under different daylights
Abstract
Deuteranomalous trichromacy, which affects medium-wavelength-sensitive cones, is more common than protanomalous trichromacy, which affects long-wavelength-sensitive cones. The aim of the present work was to test the extent to which these two kinds of anomalous trichromacy affect surface-color judgments in the natural world. Simulations of 18 natural scenes under different daylight illuminants were presented on a high-resolution color monitor to 7 deuteranomalous, 7 protanomalous, and 12 normal trichromatic observers, who had to discriminate between reflectance and illuminant changes in the images. Observers' ability to judge surface color was quantified by a standard color-constancy index. Deuteranomalous trichromats performed as well as normal trichromats, but protanomalous trichromats performed more poorly than both. The results are considered in relation to the spectral coverage of cones, rod intrusion, and the characterization of anomalous trichromacy by the Rayleigh match.
Figures


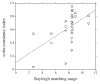
 and first illuminant 4000 K
and first illuminant 4000 K  , and for deuteranomalous trichromats with first illuminant 25000 K
, and for deuteranomalous trichromats with first illuminant 25000 K  and first illuminant 4000 K
and first illuminant 4000 K  .The dotted line is a linear regression, with slope equal to 0.065 and SE of 0.022.
.The dotted line is a linear regression, with slope equal to 0.065 and SE of 0.022.Similar articles
-
Color constancy of red-green dichromats and anomalous trichromats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Apr;51(4):2286-93. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4576. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19892868 Free PMC article.
-
Protanopic observers show nearly normal color constancy with natural reflectance spectra.Vis Neurosci. 2004 May-Jun;21(3):347-51. doi: 10.1017/s0952523804213451. Vis Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15518212 Free PMC article.
-
Color constancy in natural scenes with and without an explicit illuminant cue.Vis Neurosci. 2006 May-Aug;23(3-4):351-6. doi: 10.1017/S0952523806233285. Vis Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16961966
-
Surface color perception and equivalent illumination models.J Vis. 2011 May 2;11(5):10.1167/11.5.1 1. doi: 10.1167/11.5.1. J Vis. 2011. PMID: 21536727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colour vision: Is colour constancy real?Curr Biol. 1999 Jul 29-Aug 12;9(15):R558-61. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80354-6. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10469555 Review.
Cited by
-
Should prospective dental students be screened for colour vision deficits?Br Dent J. 2016 Sep 9;221(5):227-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2016.633. Br Dent J. 2016. PMID: 27608568
-
Coloured filters can simulate colour deficiency in normal vision but cannot compensate for congenital colour vision deficiency.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 1;12(1):11140. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13877-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35778454 Free PMC article.
-
Color constancy of red-green dichromats and anomalous trichromats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Apr;51(4):2286-93. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4576. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19892868 Free PMC article.
-
Color constancy in natural scenes explained by global image statistics.Vis Neurosci. 2006 May-Aug;23(3-4):341-9. doi: 10.1017/S0952523806233455. Vis Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16961965 Free PMC article.
-
Little information loss with red-green color deficient vision in natural environments.iScience. 2023 Jul 18;26(8):107421. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107421. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37593460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano K, Foster DH, Nascimento SMC. Red-green colour deficiency and colour constancy under orthogonal-daylight changes. In: Mollon JD, Pokorny J, Knoblauch K, editors. Normal and defective colour vision. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2003. pp. 225–230.
-
- Arend LE, Jr., Reeves A, Schirillo J, Goldstein R. Simultaneous color constancy: papers with diverse Munsell values. Journal of the Optical Society of America A-Optics Image Science and Vision. 1991;8:661–672. - PubMed
-
- Birch J. Diagnosis of Defective Colour Vision. London: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

