Tissue remodeling during maturation of the Drosophila wing
- PMID: 16962574
- PMCID: PMC1828914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.011
Tissue remodeling during maturation of the Drosophila wing
Abstract
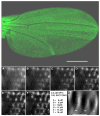
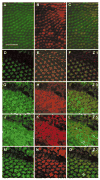
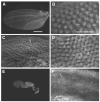
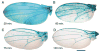
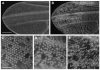
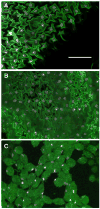
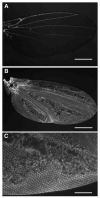
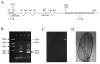
The final step in morphogenesis of the adult fly is wing maturation, a process not well understood at the cellular level due to the impermeable and refractive nature of cuticle synthesized some 30 h prior to eclosion from the pupal case. Advances in GFP technology now make it possible to visualize cells using fluorescence after cuticle synthesis is complete. We find that, between eclosion and wing expansion, the epithelia within the folded wing begin to delaminate from the cuticle and that delamination is complete when the wing has fully expanded. After expansion, epithelial cells lose contact with each other, adherens junctions are disrupted, and nuclei become pycnotic. The cells then change shape, elongate, and migrate from the wing into the thorax. During wing maturation, the Timp gene product, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases, and probably other components of an extracellular matrix are expressed that bond the dorsal and ventral cuticular surfaces of the wing following migration of the cells. These steps are dissected using the batone and Timp genes and ectopic expression of alphaPS integrin, inhibitors of Armadillo/beta-catenin nuclear activity and baculovirus caspase inhibitor p35. We conclude that an epithelial-mesenchymal transition is responsible for epithelial delamination and dissolution.
Figures
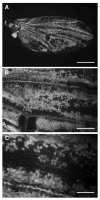
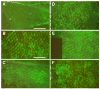
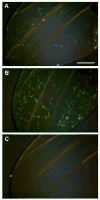
Similar articles
-
Bursicon signaling mutations separate the epithelial-mesenchymal transition from programmed cell death during Drosophila melanogaster wing maturation.Genetics. 2008 Oct;180(2):885-93. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.092908. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18780731 Free PMC article.
-
Hemocytes are essential for wing maturation in Drosophila melanogaster.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Aug 28;98(18):10190-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.181338998. Epub 2001 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11504926 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct spatial and temporal functions for PS integrins during Drosophila wing morphogenesis.Development. 1996 Oct;122(10):3307-17. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.10.3307. Development. 1996. PMID: 8898242
-
Role of the PS integrins in Drosophila development.Immunol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;73(6):558-64. doi: 10.1038/icb.1995.89. Immunol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 8713479 Review.
-
The wing and the eye: a parsimonious theory for scaling and growth control?Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2015 Nov-Dec;4(6):591-608. doi: 10.1002/wdev.195. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26108346 Review.
Cited by
-
A collective form of cell death requires homeodomain interacting protein kinase.J Cell Biol. 2007 Aug 13;178(4):567-74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200702125. Epub 2007 Aug 6. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17682052 Free PMC article.
-
Planar cell polarity and tissue design: Shaping the Drosophila wing membrane.Fly (Austin). 2011 Oct-Dec;5(4):316-21. doi: 10.4161/fly.5.4.15836. Epub 2011 May 4. Fly (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21540638 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanics of Drosophila wing deployment.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 11;15(1):10577. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54527-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39663353 Free PMC article.
-
Competing activities of heterotrimeric G proteins in Drosophila wing maturation.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 23;5(8):e12331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012331. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808795 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic background and GxE interactions modulate the penetrance of a naturally occurring wing mutation in Drosophila melanogaster.G3 (Bethesda). 2013 Nov 6;3(11):1893-901. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.007831. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 24002866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Algeciras-Schimnich A, Barnhart BC, Peter ME. Apoptosis-independent functions of killer caspases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14:721–726. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod JD, Matsuno K, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Perrimon N. Interaction between Wingless and Notch signaling pathways mediated by Dishevelled. Science. 1996;271:1826–1832. - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge SP, Bownes M. Staging the metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morph. 1981;66:57–80. - PubMed
-
- Baker JD, McNabb SL, Truman JW. The hormonal coordination of behavior and physiology at adult ecdysis in Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Biol. 1999;202:3037–3048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

