A conserved tetranucleotide repeat is necessary for wild-type expression of the Moraxella catarrhalis UspA2 protein
- PMID: 16963572
- PMCID: PMC1636323
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01204-06
A conserved tetranucleotide repeat is necessary for wild-type expression of the Moraxella catarrhalis UspA2 protein
Abstract
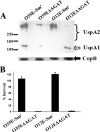
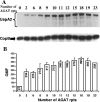
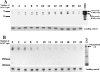
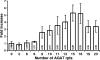
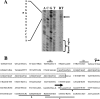
The UspA2 protein has been shown to be directly involved in the serum-resistant phenotype of Moraxella catarrhalis. The predicted 5'-untranslated regions (UTR) of the uspA2 genes in several different M. catarrhalis strains were shown to contain various numbers (i.e., 6 to 23) of a heteropolymeric tetranucleotide (AGAT) repeat. Deletion of the AGAT repeats from the uspA2 genes in the serum-resistant M. catarrhalis strains O35E and O12E resulted in a drastic reduction in UspA2 protein expression and serum resistance. PCR and transformation were used to construct a series of M. catarrhalis O12E strains that differed only in the number of AGAT repeats in their uspA2 genes. Expression of UspA2 was maximal in the presence of 18 AGAT repeats, although serum resistance attained wild-type levels in the presence of as few as nine AGAT repeats. Increased UspA2 expression was correlated with both increased binding of vitronectin and decreased binding of polymerized C9. Real-time reverse transcription-PCR analysis showed that changes in the number of AGAT repeats affected the levels of uspA2 mRNA, with 15 to 18 AGAT repeats yielding maximal levels. Primer extension analysis indicated that these AGAT repeats were contained in the 5'-UTR of the uspA2 gene. The mRNA transcribed from a uspA2 gene containing 18 AGAT repeats was found to have a longer half-life than that transcribed from a uspA2 gene lacking AGAT repeats. These data confirm that the presence of the AGAT repeats in the 5'-UTR of the uspA2 gene is necessary for both normal expression of the UspA2 protein and serum resistance.
Figures


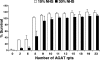
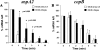

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

