Identifying gene regulatory elements by genomic microarray mapping of DNaseI hypersensitive sites
- PMID: 16963707
- PMCID: PMC1581440
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.5373606
Identifying gene regulatory elements by genomic microarray mapping of DNaseI hypersensitive sites
Abstract
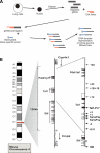
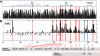
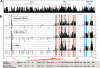
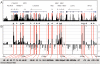
The identification of cis-regulatory elements is central to understanding gene transcription. Hypersensitivity of cis-regulatory elements to digestion with DNaseI remains the gold-standard approach to locating such elements. Traditional methods used to identify DNaseI hypersensitive sites are cumbersome and can only be applied to short stretches of DNA at defined locations. Here we report the development of a novel genomic array-based approach to DNaseI hypersensitive site mapping (ADHM) that permits precise, large-scale identification of such sites from as few as 5 million cells. Using ADHM we identified all previously recognized hematopoietic regulatory elements across 200 kb of the mouse T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia-1 (Tal1) locus, and, in addition, identified two novel elements within the locus, which show transcriptional regulatory activity. We further validated the ADHM protocol by mapping the DNaseI hypersensitive sites across 250 kb of the human TAL1 locus in CD34+ primary stem/progenitor cells and K562 cells and by mapping the previously known DNaseI hypersensitive sites across 240 kb of the human alpha-globin locus in K562 cells. ADHM provides a powerful approach to identifying DNaseI hypersensitive sites across large genomic regions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of cell type-specific and ubiquitous chromatin regulatory structures in the human genome.PLoS Genet. 2007 Aug;3(8):e136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030136. Epub 2007 Jul 2. PLoS Genet. 2007. PMID: 17708682 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time PCR mapping of DNaseI-hypersensitive sites using a novel ligation-mediated amplification technique.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(8):e56. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm108. Epub 2007 Mar 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17389645 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping regulatory elements by DNaseI hypersensitivity chip (DNase-Chip).Methods Mol Biol. 2009;556:177-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-192-9_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19488879
-
Advances of DNase-seq for mapping active gene regulatory elements across the genome in animals.Gene. 2018 Aug 15;667:83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.033. Epub 2018 May 14. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29772251 Review.
-
Distant sequences which regulate globin genes.Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;191:29-48. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985. PMID: 2996023 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin profiling across the human tumour necrosis factor gene locus reveals a complex, cell type-specific landscape with novel regulatory elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Sep;36(15):4845-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn444. Epub 2008 Jul 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18653526 Free PMC article.
-
Endoglin expression in blood and endothelium is differentially regulated by modular assembly of the Ets/Gata hemangioblast code.Blood. 2008 Dec 1;112(12):4512-22. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-157560. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18805961 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of Elf-1: locus-wide analysis reveals four distinct promoters, a tissue-specific enhancer, control by PU.1 and the importance of Elf-1 downregulation for erythroid maturation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6363-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq490. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20525788 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of CTCF-associated chromatin neighborhood inhibits TAL1-driven oncogenic transcription program and leukemogenesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 6;48(6):3119-3133. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa098. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32086528 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence composition similarities with the 7SL RNA are highly predictive of functional genomic features.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Aug;38(15):4907-16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq234. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20392819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aplan P.D., Lombardi D.P., Ginsberg A.M., Cossman J., Bertness V.L., Kirsch I.R., Lombardi D.P., Ginsberg A.M., Cossman J., Bertness V.L., Kirsch I.R., Ginsberg A.M., Cossman J., Bertness V.L., Kirsch I.R., Cossman J., Bertness V.L., Kirsch I.R., Bertness V.L., Kirsch I.R., Kirsch I.R. Disruption of the human SCL locus by “illegitimate” V-(D)-J recombinase activity. Science. 1990;250:1426–1429. - PubMed
-
- Bockamp E.O., McLaughlin F., Murrell A.M., Göttgens B., Robb L., Begley C.G., Green A.R., McLaughlin F., Murrell A.M., Göttgens B., Robb L., Begley C.G., Green A.R., Murrell A.M., Göttgens B., Robb L., Begley C.G., Green A.R., Göttgens B., Robb L., Begley C.G., Green A.R., Robb L., Begley C.G., Green A.R., Begley C.G., Green A.R., Green A.R. Lineage-restricted regulation of the murine SCL/TAL-1 promoter. Blood. 1995;86:1502–1514. - PubMed
-
- Bockamp E.O., McLaughlin F., Göttgens B., Murrell A.M., Elefanty A.G., Green A.R., McLaughlin F., Göttgens B., Murrell A.M., Elefanty A.G., Green A.R., Göttgens B., Murrell A.M., Elefanty A.G., Green A.R., Murrell A.M., Elefanty A.G., Green A.R., Elefanty A.G., Green A.R., Green A.R. Distinct mechanisms direct SCL/tal-1 expression in erythroid cells and CD34 positive primitive myeloid cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:8781–8790. - PubMed
-
- Bockamp E.O., Fordham J.L., Göttgens B., Murrell A.M., Sanchez M.J., Green A.R., Fordham J.L., Göttgens B., Murrell A.M., Sanchez M.J., Green A.R., Göttgens B., Murrell A.M., Sanchez M.J., Green A.R., Murrell A.M., Sanchez M.J., Green A.R., Sanchez M.J., Green A.R., Green A.R. Transcriptional regulation of the stem cell leukemia gene by PU.1 and Elf-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:29032–29042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
