Association of nucleoid proteins with coding and non-coding segments of the Escherichia coli genome
- PMID: 16963779
- PMCID: PMC1636352
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl542
Association of nucleoid proteins with coding and non-coding segments of the Escherichia coli genome
Abstract
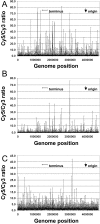
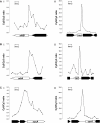
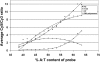
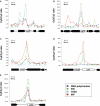
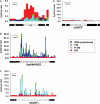
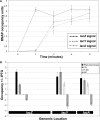
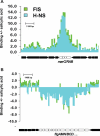
The Escherichia coli chromosome is condensed into an ill-defined structure known as the nucleoid. Nucleoid-associated DNA-binding proteins are involved in maintaining this structure and in mediating chromosome compaction. We have exploited chromatin immunoprecipitation and high-density microarrays to study the binding of three such proteins, FIS, H-NS and IHF, across the E.coli genome in vivo. Our results show that the distribution of these proteins is biased to intergenic parts of the genome, and that the binding profiles overlap. Hence some targets are associated with combinations of bound FIS, H-NS and IHF. In addition, many regions associated with FIS and H-NS are also associated with RNA polymerase.
Figures

References
-
- Sekinger E.A., Moqtaderi Z., Struhl K. Intrinsic histone–DNA interactions and low nucleosome density are important for preferential accessibility of promoter regions in yeast. Mol. Cell. 2005;18:735–448. - PubMed
-
- Yuan G.C., Liu Y.J., Dion M.F., Slack M.D., Wu L.F., Altschuler S.J., Rando O.J. Genome-scale identification of nucleosome positions in S.cerevisiae. Science. 2005;309:626–630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

