The hedgehog regulated oncogenes Gli1 and Gli2 block myoblast differentiation by inhibiting MyoD-mediated transcriptional activation
- PMID: 16964293
- PMCID: PMC3325095
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209891
The hedgehog regulated oncogenes Gli1 and Gli2 block myoblast differentiation by inhibiting MyoD-mediated transcriptional activation
Abstract
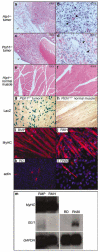
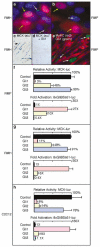
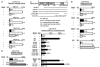
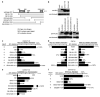
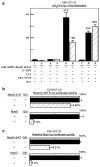
The mechanism by which activation of the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway modulates differentiation and promotes oncogenesis in specific tissues is poorly understood. We therefore, analysed rhabdomyosarcomas from mice that were haploinsufficient for the Hh-binding protein, Hip1, or for the Hh receptor, Patched 1 (Ptch1). Transfection of the Hh-regulated transcription factor Gli1, which is expressed in a subset of mouse and human rhabdomyosarcomas, suppressed differentiation of myogenic rhabdomyosarcoma lines generated from Hip1+/- and Ptch1+/- mice. The closely related factor, Gli2, had similar effects. Gli1 and Gli2 inhibited myogenesis by repressing the capacity of MyoD to activate transcription. Deletion analysis of Gli1 indicated that multiple domains of Gli1 are required for efficient inhibition of MyoD. Gli1 reduced the ability of MyoD to heterodimerize with E12 and bind DNA, providing one mechanism whereby the Gli proteins modulate the activity of MyoD. This novel activity of Gli proteins provides new insights into how Hh signaling modulates terminal differentiation through inhibition of tissue-specific factors such as MyoD. This mechanism may contribute to the broad role of Hh signaling and the Gli proteins in differentiation decisions and cancer formation.
Figures

References
-
- Amthor H, Christ B, Patel K. A molecular mechanism enabling continuous embryonic muscle growth –a balance between proliferation and differentiation. Development. 1999;126:1041–1053. - PubMed
-
- Aszterbaum M, Epstein J, Oro A, Douglas V, LeBoit PE, Scott MP, et al. Ultraviolet and ionizing radiation enhance the growth of BCCs and trichoblastomas in patched heterozygous knockout mice. Nat Med. 1999;5:1285–1291. - PubMed
-
- Aza-Blanc P, Lin HY, Ruiz i Altaba A, Kornberg TB. Expression of the vertebrate Gli proteins in Drosophila reveals a distribution of activator and repressor activities. Development. 2000;127:4293–4301. - PubMed
-
- Azmi S, Sun H, Ozog A, Taneja R. mSharp-1/DEC2, a basic helix-loop-helix protein functions as a transcriptional repressor of E box activity and Stra13 expression. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:20098–20109. - PubMed
-
- Bai CB, Joyner AL. Gli1 can rescue the in vivo function of Gli2. Development. 2001;128:5161–5172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

