Human bocavirus in French children
- PMID: 16965707
- PMCID: PMC3291226
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1708.060213.
Human bocavirus in French children
Abstract
Human bocavirus (HBoV), a new member of the genus Bocavirus in the family Parvoviridae, has been recently associated with respiratory tract infections. We report the epidemiologic and clinical features observed from a 1-year retrospective study of HBoV infection in young children hospitalized with a respiratory tract infection.
Figures
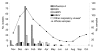

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
