The elementary unit of store-operated Ca2+ entry: local activation of CRAC channels by STIM1 at ER-plasma membrane junctions
- PMID: 16966423
- PMCID: PMC2064336
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200604015
The elementary unit of store-operated Ca2+ entry: local activation of CRAC channels by STIM1 at ER-plasma membrane junctions
Abstract
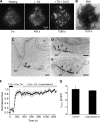
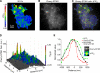
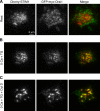
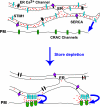
The activation of store-operated Ca(2+) entry by Ca(2+) store depletion has long been hypothesized to occur via local interactions of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and plasma membrane, but the structure involved has never been identified. Store depletion causes the ER Ca(2+) sensor stromal interacting molecule 1 (STIM1) to form puncta by accumulating in junctional ER located 10-25 nm from the plasma membrane (see Wu et al. on p. 803 of this issue). We have combined total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy and patch-clamp recording to localize STIM1 and sites of Ca(2+) influx through open Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels in Jurkat T cells after store depletion. CRAC channels open only in the immediate vicinity of STIM1 puncta, restricting Ca(2+) entry to discrete sites comprising a small fraction of the cell surface. Orai1, an essential component of the CRAC channel, colocalizes with STIM1 after store depletion, providing a physical basis for the local activation of Ca(2+) influx. These studies reveal for the first time that STIM1 and Orai1 move in a coordinated fashion to form closely apposed clusters in the ER and plasma membranes, thereby creating the elementary unit of store-operated Ca(2+) entry.
Figures
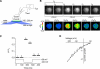
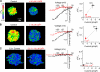
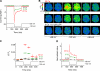

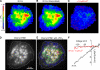
References
-
- Al-Mohanna, F.A., E.J. Pettit, and M.B. Hallett. 1997. Does actin polymerization status modulate Ca2+ storage in human neutrophils? Release and coalescence of Ca2+ stores by cytochalasins. Exp. Cell Res. 234:379–387. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, H., W.J. Lederer, and M.B. Cannell. 1993. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 262:740–744. - PubMed
-
- Fagan, K.A., R. Mahey, and D.M. Cooper. 1996. Functional co-localization of transfected Ca2+-stimulable adenylyl cyclases with capacitative Ca2+ entry sites. J. Biol. Chem. 271:12438–12444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

