Clinical utility and safety of a protocol for noncardiac and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of patients with permanent pacemakers and implantable-cardioverter defibrillators at 1.5 tesla
- PMID: 16966586
- PMCID: PMC3410556
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.607655
Clinical utility and safety of a protocol for noncardiac and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of patients with permanent pacemakers and implantable-cardioverter defibrillators at 1.5 tesla
Abstract
Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an important diagnostic modality currently unavailable for millions of patients because of the presence of implantable cardiac devices. We sought to evaluate the diagnostic utility and safety of noncardiac and cardiac MRI at 1.5T using a protocol that incorporates device selection and programming and limits the estimated specific absorption rate of MRI sequences.
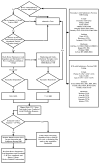
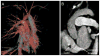
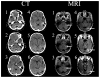
Methods and results: Patients with no imaging alternative and with devices shown to be MRI safe by in vitro phantom and in vivo animal testing were enrolled. Of 55 patients who underwent 68 MRI studies, 31 had a pacemaker, and 24 had an implantable defibrillator. Pacing mode was changed to "asynchronous" for pacemaker-dependent patients and to "demand" for others. Magnet response and tachyarrhythmia functions were disabled. Blood pressure, ECG, oximetry, and symptoms were monitored. Efforts were made to limit the system-estimated whole-body average specific absorption rate to 2.0 W/kg (successful in >99% of sequences) while maintaining the diagnostic capability of MRI. No episodes of inappropriate inhibition or activation of pacing were observed. There were no significant differences between baseline and immediate or long-term (median 99 days after MRI) sensing amplitudes, lead impedances, or pacing thresholds. Diagnostic questions were answered in 100% of nonthoracic and 93% of thoracic studies. Clinical findings included diagnosis of vascular abnormalities (9 patients), diagnosis or staging of malignancy (9 patients), and assessment of cardiac viability (13 patients).
Conclusions: Given appropriate precautions, noncardiac and cardiac MRI can potentially be safely performed in patients with selected implantable pacemaker and defibrillator systems.
Figures

Comment in
-
Food and Drug Administration perspective: Magnetic resonance imaging of pacemaker and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator patients.Circulation. 2006 Sep 19;114(12):1232-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.647800. Circulation. 2006. PMID: 16982951 No abstract available.
References
-
- Quint DJ. Indications for emergent MRI of the central nervous system. JAMA. 2000;283:853–855. - PubMed
-
- Pennell DJ, Sechtem UP, Higgins CB, Manning WJ, Pohost GM, Rademakers FE, van Rossum AC, Shaw LJ, Yucel EK. Clinical indications for cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR): Consensus Panel report. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:1940 –1965. - PubMed
-
- Martin ET, Coman JA, Shellock FG, Pulling CC, Fair R, Jenkins K. Magnetic resonance imaging and cardiac pacemaker safety at 1.5-Tesla. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:1315–1324. - PubMed
-
- Essebag V, Eisenberg MJ. Expanding indications for defibrillators after myocardial infarction: risk stratification and cost effectiveness. Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2003;7:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Brown DW, Croft JB, Giles WH, Anda RF, Mensah GA. Epidemiology of pacemaker procedures among Medicare enrollees in 1990, 1995, and 2000. Am J Cardiol. 2005;95:409–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

