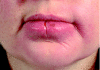
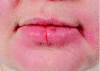
Anti-TNF-alpha therapy for orofacial granulomatosis: proceed with caution
- PMID: 16966709
- PMCID: PMC1856417
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.099143
Anti-TNF-alpha therapy for orofacial granulomatosis: proceed with caution
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
References
-
- Hegarty A, Hodgson T, Porter S. Thalidomide for the treatment of recalcitrant oral Crohn's diease and orofacial granulomatosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 200395576–585. - PubMed
-
- Mahadevan U, Sandborn W J. Infliximab for the treatment of orofacial Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2001738–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources