The C-terminus of murine S100A9 protein inhibits hyperalgesia induced by the agonist peptide of protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2)
- PMID: 16967049
- PMCID: PMC1978433
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706884
The C-terminus of murine S100A9 protein inhibits hyperalgesia induced by the agonist peptide of protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2)
Abstract
Background and purpose: S100A9 protein induces anti-nociception in rodents, in different experimental models of inflammatory pain. Herein, we investigated the effects of a fragment of the C-terminus of S100A9 (mS100A9p), on the hyperalgesia induced by serine proteases, through the activation of protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2).
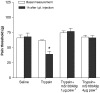
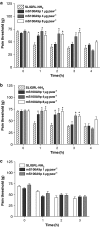
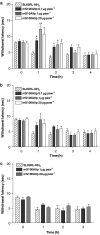
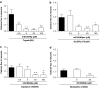
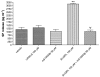
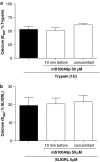
Experimental approach: Mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia induced by PAR2 agonists (SLIGRL-NH2 and trypsin) was measured in rats submitted to the paw pressure or plantar tests, and Egr-1 expression was determined by immunohistochemistry in rat spinal cord dorsal horn. Calcium flux in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK), which naturally express PAR2, in Kirsten virus-transformed kidney cells, transfected (KNRK-PAR2) or not (KNRK) with PAR2, and in mouse dorsal root ganglia neurons (DRG) was measured by fluorimetric methods.
Key results: mS100A9p inhibited mechanical hyperalgesia induced by trypsin, without modifying its enzymatic activity. Mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia induced by SLIGRL-NH2 were inhibited by mS100A9p. SLIGRL-NH2 enhanced Egr-1 expression, a marker of nociceptor activation, and this effect was inhibited by concomitant treatment with mS100A9p. mS100A9p inhibited calcium mobilization in DRG neurons in response to the PAR2 agonists trypsin and SLIGRL-NH2, but also in response to capsaicin and bradykinin, suggesting a direct effect of mS100A9 on sensory neurons. No effect on the calcium flux induced by trypsin or SLIGRL in HEK cells or KNRK-PAR2 cells was observed.
Conclusions and implications: These data demonstrate that mS100A9p interferes with mechanisms involved in nociception and hyperalgesia and modulates, possibly directly on sensory neurons, the PAR2-induced nociceptive signal.
Figures


References
-
- Aguiar-Passeti T, Postol E, Sorg C, Mariano M. Epithelioid cells from foreign-body granuloma selectively express the calcium-binding protein MRP-14, a novel down-regulatory molecule of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol. 1997;62:852–858. - PubMed
-
- Buritova J, Honore P, Besson JM. Indomethacin reduces both Krox-24 expression in the rat lumbar spinal cord and inflammatory signs following intraplantar carrageenan. Brain Res. 1995;674:211–220. - PubMed
-
- Brun JG, Haland G, Haga HJ, Fagerhol MK, Jonsson R. Effects of calprotectin in avridine-induced arthritis. APMIS. 1995;103:233–240. - PubMed
-
- Brun JG, Jonsson R, Haga HJ. Measurement of plasma calprotectin as an indicator of arthritis and disease activity in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:733–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

