Sustained contraction and loss of NO production in TGFbeta1-treated endothelial cells
- PMID: 16967050
- PMCID: PMC1978430
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706883
Sustained contraction and loss of NO production in TGFbeta1-treated endothelial cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFbeta1) is generated in atherosclerotic and injured vessel walls. We examined whether the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transdifferentiation induced by TGFbeta1 affects endothelial functions.
Experimental approach: Bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) were treated with 3 ng ml(-1) TGFbeta1 for 7 days. Contraction of TGFbeta1-treated BAECs was assessed by collagen gel contraction assay. Protein expression and phosphorylation were assessed by Western blotting. Intracellular Ca2+ concentration and NO production were measured using fura2 and DAF-2, respectively.
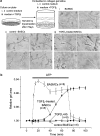
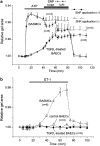
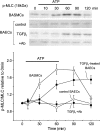
Key results: TGFbeta1-treated BAECs showed dense actin fibers and expressed smooth muscle marker proteins; they also changed into smooth muscle-like, spindle-shaped cells in collagen gel cultures. ATP (10 microM) induced a gradual contraction of collagen gels containing TGFbeta1-treated BAECs but not of gels containing control BAECs. ATP-induced contraction of TGFbeta1-treated BAECs was not reversed by the removal of ATP but was partially suppressed by a high concentration of sodium nitroprusside (1 microM). TGFbeta1-treated BAECs showed sustained phosphorylation of myosin light chain in response to ATP and low levels of basal MYPT1 expression. ATP-induced Ca2+ transients as well as eNOS protein expression were not affected by TGFbeta1 in BAECs. However, ATP-induced NO production was significantly reduced in TGFbeta1-treated BAECs. Anti-TGFbeta1 antibody abolished all of these TGFbeta1-induced changes in BAECs.
Conclusions and implications: Mesenchymal transdifferentiation induced by TGFbeta1 leads to sustained contraction and reduced NO production in endothelial cells. Such effects, therefore, would not be beneficial for vascular integrity.
Figures





References
-
- Arciniegas E, Neves CY, Carrillo LM, Zambrano EA, Ramirez R. Endothelial-mesenchymal transition occurs during embryonic pulmonary artery development. Endothelium. 2005;12:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Arciniegas E, Sutton AB, Allen TD, Schor AM. Transforming growth factor β1 promotes the differentiation of endothelial cells into smooth muscle-like cells in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1992;103:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Ehrlich HP, Rockwell WB, Cornwell TL, Rajaratnam JB. Demonstration of a direct role for myosin light chain kinase in fibroblast-populated collagen lattice contraction. J Cell Physiol. 1991;146:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

