Protease-modulated cellular uptake of quantum dots
- PMID: 16968013
- PMCID: PMC2553895
- DOI: 10.1021/nl0611586
Protease-modulated cellular uptake of quantum dots
Abstract
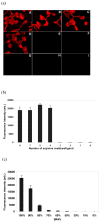
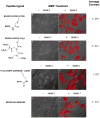
Quantum dots (QDs) are often cell-impermeable and require transporters to facilitate crossing over cell membranes. Here we present a simple and versatile method that utilizes enzymes, matrix metalloprotease 2 (MMP-2) and MMP-7, to modulate the cellular uptake of QDs. QD-peptide conjugates could be efficiently taken up into cells after the MMP treatment. This enzyme-modulated cellular uptake of QDs may be applied to other nanoparticles for biological imaging and selective drug delivery into tumor cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PEGylated and MMP-2 specifically dePEGylated quantum dots: comparative evaluation of cellular uptake.Langmuir. 2009 Feb 3;25(3):1645-50. doi: 10.1021/la803542v. Langmuir. 2009. PMID: 19117377
-
Bioconjugation of luminescent silicon quantum dots for selective uptake by cancer cells.Bioconjug Chem. 2011 Jun 15;22(6):1081-8. doi: 10.1021/bc100552p. Epub 2011 May 18. Bioconjug Chem. 2011. PMID: 21473652
-
Quantum dots based molecular beacons for in vitro and in vivo detection of MMP-2 on tumor.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Nov 15;61:512-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.05.035. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 24951921
-
Peptide coated quantum dots for biological applications.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2006 Dec;5(4):231-8. doi: 10.1109/tnb.2006.886563. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2006. PMID: 17181021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantum dot-based nanoprobes for in vivo targeted imaging.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Dec;13(10):1549-67. doi: 10.2174/1566524013666131111121733. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24206136 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis, and imaging of an activatable photoacoustic probe.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Aug 18;132(32):11264-9. doi: 10.1021/ja104000a. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20698693 Free PMC article.
-
Activatable and Cell-Penetrable Multiplex FRET Nanosensor for Profiling MT1-MMP Activity in Single Cancer Cells.Nano Lett. 2015 Aug 12;15(8):5025-32. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01047. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Nano Lett. 2015. PMID: 26203778 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical biology for understanding matrix metalloproteinase function.Chembiochem. 2012 Sep 24;13(14):2002-20. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201200298. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Chembiochem. 2012. PMID: 22933318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging methods to evaluate tumor microenvironment factors affecting nanoparticle drug delivery and antitumor response.Cancer Drug Resist. 2021;4(2):382-413. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.94. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34796317 Free PMC article.
-
Polydopamine-based surface modification for the development of peritumorally activatable nanoparticles.Pharm Res. 2013 Aug;30(8):1956-67. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1039-y. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23609560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP. Science. 1998;281:2013–2016. - PubMed
-
- Chan WCW, Nie SM. Science. 1998;281:2016–2018. - PubMed
-
- Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H. Nat Mater. 2005;4:435–446. - PubMed
-
- Jaiswal JK, Simon SM. Trends in Cell Biology. 2004;14:497–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

