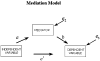
Mediation analysis
- PMID: 16968208
- PMCID: PMC2819368
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085542
Mediation analysis
Abstract
Mediating variables are prominent in psychological theory and research. A mediating variable transmits the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable. Differences between mediating variables and confounders, moderators, and covariates are outlined. Statistical methods to assess mediation and modern comprehensive approaches are described. Future directions for mediation analysis are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Aiken LS, West SG. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1991.
-
- Alwin DF, Hauser RM. The decomposition of effects in path analysis. Am Sociol Rev. 1975;40:37–47.
-
- Angrist JD, Imbens GW, Rubin DB. Identification of causal effects using instrumental variables (with commentary) J Am Stat Assoc. 1996;91:444–72.
-
- Arbuckle JL. AMOS User’s Guide: Version 3.6. Chicago: Smallwaters; 1997.
-
- Arminger G. Linear stochastic differential equation models for panel data with unobserved variables. Sociol Methodol. 1986;16:187–212.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical