Both Fcgamma and complement receptors mediate transfer of immune complexes from erythrocytes to human macrophages under physiological flow conditions in vitro
- PMID: 16968408
- PMCID: PMC1809732
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03174.x
Both Fcgamma and complement receptors mediate transfer of immune complexes from erythrocytes to human macrophages under physiological flow conditions in vitro
Abstract
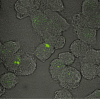
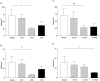
Abnormal clearance by the mononuclear phagocytic system of immune complexes (IC) is important in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We have developed an in vitro model to investigate the cellular mechanisms involved in the transfer of soluble IC from erythrocytes to human macrophages under physiological flow conditions. In this assay, erythrocytes bearing fluorescently labelled IC are perfused over monolayers of human monocytes or monocyte-derived macrophages in a parallel-plate flow chamber, and transfer quantified using confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. Using aggregated human IgG as a model IC, we have been able to demonstrate transfer of IC from erythrocytes to macrophages. Blocking studies with specific neutralizing antibodies have shown that both complement and Fcgamma receptors are required for IC transfer. Blockade of CR4 (alpha(x)beta(2) integrin), FcgammaRIIa or FcgammaRIII reduced transfer, while anti-CR3 (alpha(m)beta(2) integrin) had no effect. Blockade of CR3, FcgammaRIIa or FcgammaRIII also reduced the number of adhesive interactions between fluorescently labelled IC-bearing erythrocytes and macrophage monolayers. Taken together with the transfer data, this suggests differing roles for these receptors in the human IC transfer reaction that includes an adhesive function which facilitates IC processing by mononuclear phagocytes. Finally, a functional effect of the FcgammaRIIa R131/H131 polymorphism, important in susceptibility to SLE, has also been demonstrated using this model. Uptake of IgG(2) but not IgG(1)-containing soluble IC was reduced by macrophages from individuals homozygous for the R131 allelic variant of the receptor.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Fcgamma receptor polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus].Rev Invest Clin. 2009 Jan-Feb;61(1):66-72. Rev Invest Clin. 2009. PMID: 19507476 Review. Spanish.
-
Factors influencing the endocytosis of immune complexes.Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1984;13:341-67. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1984. PMID: 6236677 Review.
-
Expression of Fcgamma and complement receptors on peripheral blood monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004 May;43(5):547-54. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh112. Epub 2004 Jan 27. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004. PMID: 14747618
-
Functional characterization of non-human primate erythrocyte immune adherence receptors: implications for the uptake of immune complexes by the cells of the mononuclear phagocytic system.Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1333-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220602. Eur J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1376254
-
Mechanism of transfer of immune complexes from red blood cell CR1 to monocytes.Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jul;89(1):8-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06869.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1385769 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of medium pH and antibody Fc fragment on the size of model immune complexes.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2013 Nov;453:286-7. doi: 10.1134/S1607672913060045. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 24385097 No abstract available.
-
Microparticles provide a novel biomarker to predict severe clinical outcomes of dengue virus infection.J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(3):1587-607. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02207-14. Epub 2014 Nov 19. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25410854 Free PMC article.
-
RBC Adherence of Immune Complexes Containing Botulinum Toxin Improves Neutralization and Macrophage Uptake.Toxins (Basel). 2017 May 19;9(5):173. doi: 10.3390/toxins9050173. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28534855 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Antibody Therapeutics by Manipulating the Fc Domain: Immunological and Structural Considerations.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2022 Jun 6;24:249-274. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-082721-024500. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2022. PMID: 35363537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arthrogenicity of type II collagen monoclonal antibodies associated with complement activation and antigen affinity.J Inflamm (Lond). 2011 Nov 4;8(1):31. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-8-31. J Inflamm (Lond). 2011. PMID: 22054174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schifferli JA, Taylor RP. Physiological and pathological aspects of circulating immune complexes. Kidney Int. 1989;35:993–1003. - PubMed
-
- Davies KA. Immune complexes and autoimmunity. In: Lahita RG, Chiorazzi N, Reeves WH, editors. Textbook of the autoimmune diseases. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2000. pp. 137–51.
-
- Craig ML, Bankovich AJ, McElhenny JL, Taylor RP. Clearance of anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies: the natural immune complex clearance mechanism. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2265–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

