Etanercept 50 mg once weekly is as effective as 25 mg twice weekly in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
- PMID: 16968715
- PMCID: PMC1798458
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.056747
Etanercept 50 mg once weekly is as effective as 25 mg twice weekly in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy, pharmacokinetics and safety of etanercept 50 mg once weekly with 25 mg twice weekly and placebo in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Methods: A 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study compared the effects of etanercept 50 mg once weekly, etanercept 25 mg twice weekly and placebo in 356 patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (3:3:1 randomisation, respectively). The primary end point was the proportion of patients achieving a response at week 12 based on the Assessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis Working Group criteria (ASAS 20). The pharmacokinetics of etanercept 50 mg once weekly and 25 mg twice weekly were analysed.
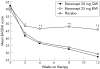
Results: Baseline characteristics and disease activity were similar among the three groups: etanercept 50 mg once weekly, etanercept 25 mg twice weekly and placebo. The percentage of patients discontinuing therapy was 9.0%, 9.3% and 13.7% for the three respective groups. ASAS 20 response at 12 weeks was achieved by 74.2% of patients with etanercept 50 mg once weekly and 71.3% of those with etanercept 25 mg twice weekly, both significantly higher than the percentage of patients taking placebo (37.3%, p<0.001). Percentages of patients with ASAS 5/6 response (70.3%, 72.0% and 27.5%, respectively; p<0.001) and those with ASAS 40 response (58.1%, 53.3% and 21.6%, respectively; p<0.001) followed a similar pattern. Significant improvement (p<0.05) was seen in measures of disease activity, back pain, morning stiffness and C reactive protein levels as early as 2 weeks. Serum etanercept exposure was similar between the etanercept groups. Incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events, including infections, was similar among all three groups, and no unexpected safety issues were identified.
Conclusions: Patients with ankylosing spondylitis can expect a comparable significant improvement in clinical outcomes with similar safety when treated with etanercept 50 mg once weekly or with 25 mg twice weekly.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DvdH was reimbursed by Wyeth, the manufacturer of etanercept, for attending several conferences and for running educational programmes, and has received research grants. JCdS was paid by Schering‐Plough Pharma for running educational programmes and served as an advisory board member for Abbott. MD received grants from Wyeth to conduct clinical trials, and also fees for consulting and for speaking at symposia organised by Wyeth. PG was reimbursed by Wyeth, the manufacturer of etanercept, for attending a conference, and received fees for speaking at another conference. FR received fees for speaking to general practitioners who have been working with our hospital over the past 5 years. JS received fees for consulting and speaking, and funds for research. LP, JSW, SF and M‐PB are employees of Wyeth Research. IvdH‐B, XJ, IO, LS, JS and DW have no competing interests.
References
-
- Wooley P H, Dutcher J, Widmer M B, Gillis S. Influence of a recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor FC fusion protein on type II collagen‐induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol 19931516602–6607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials