An integrated systems approach for understanding cellular responses to gamma radiation
- PMID: 16969339
- PMCID: PMC1681521
- DOI: 10.1038/msb4100091
An integrated systems approach for understanding cellular responses to gamma radiation
Abstract
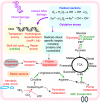
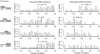
Cellular response to stress entails complex mRNA and protein abundance changes, which translate into physiological adjustments to maintain homeostasis as well as to repair and minimize damage to cellular components. We have characterized the response of the halophilic archaeon Halobacterium salinarum NRC-1 to (60)Co ionizing gamma radiation in an effort to understand the correlation between genetic information processing and physiological change. The physiological response model we have constructed is based on integrated analysis of temporal changes in global mRNA and protein abundance along with protein-DNA interactions and evolutionarily conserved functional associations. This systems view reveals cooperation among several cellular processes including DNA repair, increased protein turnover, apparent shifts in metabolism to favor nucleotide biosynthesis and an overall effort to repair oxidative damage. Further, we demonstrate the importance of time dimension while correlating mRNA and protein levels and suggest that steady-state comparisons may be misleading while assessing dynamics of genetic information processing across transcription and translation.
Figures

References
-
- Allers T, Ngo HP (2003) Genetic analysis of homologous recombination in Archaea: Haloferax volcanii as a model organism. Biochem Soc Trans 31: 706–710 - PubMed
-
- Baliga NS, Goo YA, Ng WV, Hood L, Daniels CJ, DasSarma S (2000) Is gene expression in Halobacterium NRC-1 regulated by multiple TBP and TFB transcription factors? Mol Microbiol 36: 1184–1185 - PubMed
-
- Cannio R, Fiorentino G, Morana A, Rossi M, Bartolucci S (2000) Oxygen: friend or foe?. Archaeal superoxide dismutases in the protection of intra- and extracellular oxidative stress. Front Biosci 5: D768–D779 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

