A full-length cDNA infectious clone of North American type 1 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus: expression of green fluorescent protein in the Nsp2 region
- PMID: 16971421
- PMCID: PMC1642622
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01032-06
A full-length cDNA infectious clone of North American type 1 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus: expression of green fluorescent protein in the Nsp2 region
Abstract
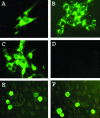
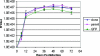
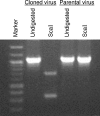
The recent emergence of a unique group of North American type 1 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in the United States presents new disease control problems for a swine industry that has already been impacted seriously by North American type 2 PRRSV. In this study, a full-length cDNA infectious clone was generated from a low-virulence North American type 1 PRRSV isolate, SD01-08. In vitro studies demonstrated that the cloned virus maintained growth properties similar to those of the parental virus. Virological, pathological, and immunological observations from animals challenged with cloned viruses were similar to those from animals challenged with the parental virus and a modified live virus vaccine. To further explore the potential use as a viral backbone for expressing foreign genes, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) was inserted into a unique deletion site located at amino acid positions 348 and 349 of the predicted Nsp2 region in the virus, and expression of the Nsp2-GFP fusion protein was visualized by fluorescent microscopy. The availability of this North American type 1 infectious clone provides an important research tool for further study of the basic viral biology and pathogenic mechanisms of this group of type 1 PRRSV in the United States.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Establishment of a DNA-launched infectious clone for a highly pneumovirulent strain of type 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus: identification and in vitro and in vivo characterization of a large spontaneous deletion in the nsp2 region.Virus Res. 2011 Sep;160(1-2):264-73. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.06.027. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 21763365
-
Generation of an infectious clone of VR-2332, a highly virulent North American-type isolate of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.J Virol. 2003 Mar;77(6):3702-11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.6.3702-3711.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12610145 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus as a vector: immunogenicity of green fluorescent protein and porcine circovirus type 2 capsid expressed from dedicated subgenomic RNAs.Virology. 2009 Jun 20;389(1-2):91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.03.036. Epub 2009 May 6. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19423145
-
In vivo growth of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus engineered nsp2 deletion mutants.Virus Res. 2010 Dec;154(1-2):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.07.024. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 20673840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The genome of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and the molecular basis of pathogenesis].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2007 Jan;23(1):79-83. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17886728 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of nonessential regions of the nsp2 protein of an attenuated vaccine strain (HuN4-F112) of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus for replication in marc-145 cell.Virol J. 2012 Aug 2;9:141. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-141. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22856599 Free PMC article.
-
Nonstructural protein 2 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus inhibits the antiviral function of interferon-stimulated gene 15.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(7):3839-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06466-11. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22258253 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence analysis of the NSP2, ORF5, and ORF7 genes of 11 PRRS virus isolates from China.Virus Genes. 2012 Oct;45(2):256-64. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0763-4. Epub 2012 May 30. Virus Genes. 2012. PMID: 22644762
-
Identification of nonessential regions of the nsp2 replicase protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strain VR-2332 for replication in cell culture.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(18):9878-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00562-07. Epub 2007 May 23. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17522233 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering the PRRS virus genome: updates and perspectives.Vet Microbiol. 2014 Dec 5;174(3-4):279-295. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.10.007. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25458419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bautista, E. M., S. M. Goyal, I. J. Soon, H. S. Joo, and J. E. Collins. 1996. Structural polypeptides of the American (VR-2332) strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Arch. Virol. 141:1357-1365. - PubMed
-
- Benfield, D. A., E. Nelson, J. E. Collins, L. Harris, S. M. Goyal, D. Robison, W. T. Christianson, R. B. Morrison, D. Gorcyca, and D. Chladek. 1992. Characterization of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 4:127-133. - PubMed
-
- Calvert, J. G., M. G. Sheppard, and S. K. W. Welch. 2003. Infectious cDNA clone of North American porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus and use thereof. U.S. patent application 20,030,157,689.
-
- Calvert, J. G., M. G. Sheppard, and S. K. W. Welch. December 2002. Infectious cDNA clone of North American porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus and use thereof. U.S. patent 6,500,662.
-
- Collins, J. E., D. A. Benfield, W. T. Christianson, L. Harris, J. C. Hennings, D. P. Shaw, S. M. Goyal, D. Gorcyca, D. Chladek, S. McCullough, R. B. Morrison, and H. S. Joo. 1992. Isolation of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332) in North America and experimental reproduction of the disease in gnotobiotic pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 4:117-126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

