Integrin signaling through Arg activates p190RhoGAP by promoting its binding to p120RasGAP and recruitment to the membrane
- PMID: 16971514
- PMCID: PMC1635390
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-02-0132
Integrin signaling through Arg activates p190RhoGAP by promoting its binding to p120RasGAP and recruitment to the membrane
Abstract
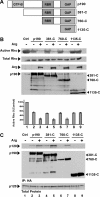
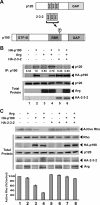
The Rho family GTPases RhoA (Rho), Rac1, and Cdc42 are essential effectors of integrin-mediated cell attachment and spreading. Rho activity, which promotes formation of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers, is inhibited upon initial cell attachment to allow sampling of the new adhesive environment. The Abl-related gene (Arg) tyrosine kinase mediates adhesion-dependent inhibition of Rho through phosphorylation and activation of the Rho inhibitor p190RhoGAP-A (p190). p190 phosphorylation promotes its binding to p120RasGAP (p120). Here, we elucidate the mechanism by which p120 binding regulates p190 activation after adhesion. We show that p190 requires its p120-binding domain to undergo Arg-dependent activation in vivo. However, p120 binding does not activate p190RhoGAP activity in vitro. Instead, activation of p190 requires recruitment to the cell periphery. Integrin-mediated adhesion promotes relocalization of p190 and p120 to the cell periphery in wild-type fibroblasts, but not in arg(-/-) fibroblasts. A dominant-negative p120 fragment blocks p190:p120 complex formation, prevents activation of p190 by adhesion, and disrupts the adhesion-dependent recruitment of p190 to the cell periphery. Our results demonstrate that integrin signaling through Arg activates p190 by promoting its association with p120, resulting in recruitment of p190 to the cell periphery where it inhibits Rho.
Figures





References
-
- Arthur W. T., Noren N. K., Burridge K. Regulation of Rho family GTPases by cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion. Biol. Res. 2002;35:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Arthur W. T., Petch L. A., Burridge K. Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Curr. Biol. 2000;10:719–722. - PubMed
-
- Barry S. T., Flinn H. M., Humphries M. J., Critchley D. R., Ridley A. J. Requirement for Rho in integrin signalling. Cell Adhes. Commun. 1997;4:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Brouns M. R., Matheson S. F., Hu K. Q., Delalle I., Caviness V. S., Silver J., Bronson R. T., Settleman J. The adhesion signaling molecule p190 RhoGAP is required for morphogenetic processes in neural development. Development. 2000;127:4891–4903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

