LET-711, the Caenorhabditis elegans NOT1 ortholog, is required for spindle positioning and regulation of microtubule length in embryos
- PMID: 16971515
- PMCID: PMC1635396
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-02-0107
LET-711, the Caenorhabditis elegans NOT1 ortholog, is required for spindle positioning and regulation of microtubule length in embryos
Abstract
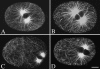
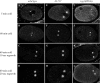
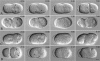
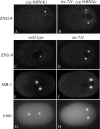
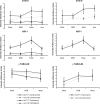
Spindle positioning is essential for the segregation of cell fate determinants during asymmetric division, as well as for proper cellular arrangements during development. In Caenorhabditis elegans embryos, spindle positioning depends on interactions between the astral microtubules and the cell cortex. Here we show that let-711 is required for spindle positioning in the early embryo. Strong loss of let-711 function leads to sterility, whereas partial loss of function results in embryos with defects in the centration and rotation movements that position the first mitotic spindle. let-711 mutant embryos have longer microtubules that are more cold-stable than in wild type, a phenotype opposite to the short microtubule phenotype caused by mutations in the C. elegans XMAP215 homolog ZYG-9. Simultaneous reduction of both ZYG-9 and LET-711 can rescue the centration and rotation defects of both single mutants. let-711 mutant embryos also have larger than wild-type centrosomes at which higher levels of ZYG-9 accumulate compared with wild type. Molecular identification of LET-711 shows it to be an ortholog of NOT1, the core component of the CCR4/NOT complex, which plays roles in the negative regulation of gene expression at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels in yeast, flies, and mammals. We therefore propose that LET-711 inhibits the expression of ZYG-9 and potentially other centrosome-associated proteins, in order to maintain normal centrosome size and microtubule dynamics during early embryonic divisions.
Figures
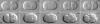

Similar articles
-
ZYG-9, TAC-1 and ZYG-8 together ensure correct microtubule function throughout the cell cycle of C. elegans embryos.J Cell Sci. 2007 Aug 15;120(Pt 16):2963-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.004812. Epub 2007 Jul 31. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17666432
-
PAR-3 and PAR-1 inhibit LET-99 localization to generate a cortical band important for spindle positioning in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Nov;18(11):4470-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0105. Epub 2007 Aug 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17761536 Free PMC article.
-
zyg-8, a gene required for spindle positioning in C. elegans, encodes a doublecortin-related kinase that promotes microtubule assembly.Dev Cell. 2001 Sep;1(3):363-75. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(01)00046-6. Dev Cell. 2001. PMID: 11702948
-
Spindle positioning during the asymmetric first cell division of Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Novartis Found Symp. 2001;237:164-75; discussion 176-81. doi: 10.1002/0470846666.ch13. Novartis Found Symp. 2001. PMID: 11444042 Review.
-
Physical Limits on the Precision of Mitotic Spindle Positioning by Microtubule Pushing forces: Mechanics of mitotic spindle positioning.Bioessays. 2017 Nov;39(11):10.1002/bies.201700122. doi: 10.1002/bies.201700122. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Bioessays. 2017. PMID: 28960439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The in vivo functional significance of PUF hub partnerships in C. elegans germline stem cells.Development. 2023 May 1;150(9):dev201705. doi: 10.1242/dev.201705. Epub 2023 May 9. Development. 2023. PMID: 37070766 Free PMC article.
-
The UBXN-2/p37/p47 adaptors of CDC-48/p97 regulate mitosis by limiting the centrosomal recruitment of Aurora A.J Cell Biol. 2013 May 13;201(4):559-75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201209107. Epub 2013 May 6. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23649807 Free PMC article.
-
Functional significance of PUF partnerships in C. elegans germline stem cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 16:2023.02.15.528708. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.15.528708. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Development. 2023 May 1;150(9):dev201705. doi: 10.1242/dev.201705. PMID: 36824876 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The spindle assembly function of Caenorhabditis elegans katanin does not require microtubule-severing activity.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 May;22(9):1550-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-12-0951. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21372175 Free PMC article.
-
Life span extension via eIF4G inhibition is mediated by posttranscriptional remodeling of stress response gene expression in C. elegans.Cell Metab. 2011 Jul 6;14(1):55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.05.010. Cell Metab. 2011. PMID: 21723504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellaiche Y., Gotta M. Heterotrimeric G proteins and regulation of size asymmetry during cell division. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005;17:658–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

