Blocking soluble tumor necrosis factor signaling with dominant-negative tumor necrosis factor inhibitor attenuates loss of dopaminergic neurons in models of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 16971520
- PMCID: PMC3707118
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1504-06.2006
Blocking soluble tumor necrosis factor signaling with dominant-negative tumor necrosis factor inhibitor attenuates loss of dopaminergic neurons in models of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
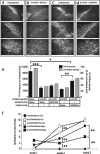
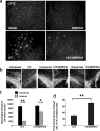
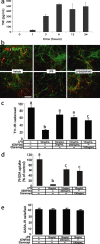
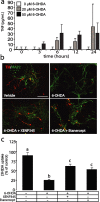
The mechanisms that trigger or contribute to loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in Parkinson's disease (PD) remain unclear and controversial. Elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in CSF and postmortem brains of PD patients and animal models of PD implicate this proinflammatory cytokine in the pathophysiology of the disease; but a role for TNF in mediating loss of DA neurons in PD has not been clearly demonstrated. Here, we report that neutralization of soluble TNF (solTNF) in vivo with the engineered dominant-negative TNF compound XENP345 (a PEGylated version of the TNF variant A145R/I97T) reduced by 50% the retrograde nigral degeneration induced by a striatal injection of the oxidative neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). XENP345 was neuroprotective only when infused into the nigra, not the striatum. XENP345/6-OHDA rats displayed attenuated amphetamine-induced rotational behavior, indicating preservation of striatal dopamine levels. Similar protective effects were observed with chronic in vivo coinfusion of XENP345 with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) into the substantia nigra, confirming a role for solTNF-dependent neuroinflammation in nigral degeneration. In embryonic rat midbrain neuron/glia cell cultures exposed to LPS, even delayed administration of XENP345 prevented selective degeneration of DA neurons despite sustained microglia activation and secretion of solTNF. XENP345 also attenuated 6-OHDA-induced DA neuron toxicity in vitro. Collectively, our data demonstrate a role for TNF in vitro and in vivo in two models of PD, and raise the possibility that delaying the progressive degeneration of the nigrostriatal pathway in humans is therapeutically feasible with agents capable of blocking solTNF in early stages of PD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peripheral administration of the selective inhibitor of soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) XPro®1595 attenuates nigral cell loss and glial activation in 6-OHDA hemiparkinsonian rats.J Parkinsons Dis. 2014;4(3):349-60. doi: 10.3233/JPD-140410. J Parkinsons Dis. 2014. PMID: 25061061 Free PMC article.
-
Cystatin C prevents degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons: in vitro and in vivo studies.Neurobiol Dis. 2005 Feb;18(1):152-65. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2004.08.012. Neurobiol Dis. 2005. PMID: 15649706
-
Intranigral lentiviral delivery of dominant-negative TNF attenuates neurodegeneration and behavioral deficits in hemiparkinsonian rats.Mol Ther. 2008 Sep;16(9):1572-9. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.146. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Mol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18628756 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Parkinson's disease: potential environmental triggers, pathways, and targets for early therapeutic intervention.Exp Neurol. 2007 Nov;208(1):1-25. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Exp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17720159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel cell death signaling pathways in neurotoxicity models of dopaminergic degeneration: relevance to oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease.Neurotoxicology. 2010 Sep;31(5):555-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2009.12.003. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Neurotoxicology. 2010. PMID: 20005250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the inflammasome in Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 12;14:957705. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.957705. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36313019 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors as potent therapeutic agents for the treatment of Parkinson disease.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Feb 20;4(2):350-60. doi: 10.1021/cn300182g. Epub 2012 Dec 5. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23421686 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic activation of proapoptotic kinase protein kinase Cδ by tumor necrosis factor α death receptor signaling in dopaminergic neurons during neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Apr 27;9:82. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-82. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22540228 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the relationship between astrocyte dysfunction and neurodegeneration in ALS using hiPSCs.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Dec;132:104562. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104562. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 31381978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nardostachys jatamansi and levodopa combination alleviates Parkinson's disease symptoms in rats through activation of Nrf2 and inhibition of NLRP3 signaling pathways.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):1175-1185. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2244176. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37559448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Samanta A, Feldmann M. TNFα. In: Oppenheim JJ, Feldmann M, editors. Cytokine reference. London: Academic; 2000. pp. 414–434.
-
- Agnholt J, Dahlerup JF, Kaltoft K. The effect of etanercept and infliximab on the production of tumour necrosis factor alpha, interferon-gamma and GM-CSF in in vivo activated intestinal T lymphocyte cultures. Cytokine. 2003;23:76–85. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Rothwell NJ. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:734–744. - PubMed
-
- Aloe L, Fiore M. TNF-alpha expressed in the brain of transgenic mice lowers central tyroxine hydroxylase immunoreactivity and alters grooming behavior. Neurosci Lett. 1997;238:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Arnett HA, Mason J, Marino M, Suzuki K, Matsushima GK, Ting JP. TNF alpha promotes proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitors and remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:1116–1122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
