Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 suppresses the ability of activated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 to stimulate neurite growth in rat primary sensory neurons
- PMID: 16971535
- PMCID: PMC6674589
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2160-06.2006
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 suppresses the ability of activated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 to stimulate neurite growth in rat primary sensory neurons
Abstract
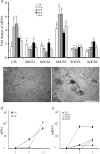
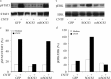
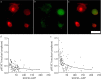
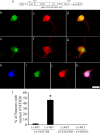
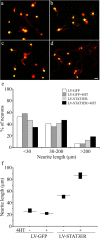
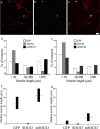
The actions of the neuropoietic cytokines are mediated by the gp130 receptor, which activates several signaling molecules including the transcription factor STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription), which, in turn, is subject to feedback inhibition by SOCS3 (suppressor of cytokine signaling). Activation of the gp130 receptor has been implicated in axonal growth particularly during regeneration, but the specific contribution of STAT3 is the subject of conflicting reports. Measurements of SOCS3 mRNA in rat dorsal root ganglia showed a significant induction in this inhibitory molecule after peripheral nerve injury. The functions of STAT3 and SOCS3 in adult rat primary sensory neurons were investigated in vitro through transduction of lentiviruses yielding a conditionally activated STAT3, native SOCS3, or a mutant SOCS3 with dominant-negative actions. The SOCS3 construct was effective in inhibiting tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in a neuroblastoma cell line and in blocking nuclear accumulation of endogenous STAT3 or of the conditionally activated STAT3 chimera in primary sensory neurons. In such neurons, transduction and activation of STAT3 enhanced neurite growth, transduction with SOCS3 reduced neurite outgrowth, and transduction with mutant SOCS3 enhanced neurite growth, at least under basal conditions. In conclusion, STAT3 signaling is beneficial to axonal growth through activating transcription of unidentified genes, and SOCS3 is detrimental to axonal growth through inhibition of STAT3 and/or other transcription factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 negative regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in platelet-derived growth factor-induced fibroblast migration.J Dermatol. 2007 Aug;34(8):523-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00325.x. J Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17683382
-
SOCS3 suppresses AP-1 transcriptional activity in neuroblastoma cells through inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008 Feb;37(2):367-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.10.010. Epub 2007 Oct 30. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18055217
-
SOCS3-mediated blockade of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway reveals its major contribution to spinal cord neuroinflammation and mechanical allodynia after peripheral nerve injury.J Neurosci. 2010 Apr 21;30(16):5754-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5007-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20410127 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS3 and STAT3, major controllers of the outcome of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Semin Immunol. 2014 Dec;26(6):518-32. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25458989 Review.
-
Ying and Yang of Stat3 in pathogenesis of aortic dissection.J Cardiol. 2021 May;77(5):471-474. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2020.10.010. Epub 2020 Nov 2. J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33148468 Review.
Cited by
-
STAT3 integrates cytokine and neurotrophin signals to promote sympathetic axon regeneration.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:272-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.06.005. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23831387 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual dimorphism in up-regulation of suppressors of cytokine signaling genes in patients with bipolar disorder.BMC Psychiatry. 2019 Dec 16;19(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2396-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31842857 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Macrophage, Dendritic Cell, and Microglial Phenotype and Function by the SOCS Proteins.Front Immunol. 2015 Oct 27;6:549. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00549. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26579124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Conditioning Sciatic Nerve Lesion Triggers a Pro-regenerative State in Primary Sensory Neurons Also of Dorsal Root Ganglia Non-associated With the Damaged Nerve.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Feb 4;13:11. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00011. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30778286 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral activation of STAT3 by phosphorylation at the tyrosine-705 (Y705) and serine-727 (S727) positions and its nuclear translocation in primary sensory neurons following unilateral sciatic nerve injury.Histochem Cell Biol. 2018 Jul;150(1):37-47. doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1656-y. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29488000
References
-
- Banerjee A, Banks AS, Nawijn MC, Chen XP, Rothman PB. Cutting edge: suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 inhibits activation of NFATp. J Immunol. 2002;168:4277–4281. - PubMed
-
- Bomze HM, Bulsara KR, Iskandar BJ, Caroni P, Skene JH. Spinal axon regeneration evoked by replacing two growth cone proteins in adult neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:38–43. - PubMed
-
- Cacalano NA, Sanden D, Johnston JA. Tyrosine-phosphorylated SOCS-3 inhibits STAT activation but binds to p120 RasGAP and activates Ras. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:460–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
