CT arteriography and venography in pulsatile tinnitus: preliminary results
- PMID: 16971601
- PMCID: PMC8139805
CT arteriography and venography in pulsatile tinnitus: preliminary results
Abstract
Background and purpose: Pulsatile tinnitus (PT), a common disorder, can be caused by a variety of otologic and vascular lesions. Various imaging modalities, including CT, MR imaging and angiography, and conventional angiography, have been used in the assessment of PT. Ideally, a single imaging study to evaluate for the largest variety of etiologies would be optimal. In our study, we examine the potential for CT arteriography and venography (CTA/V) in the evaluation of PT.
Methods: Sixteen patients with PT were prospectively evaluated by an otolaryngologist, had a normal otologic examination, and were referred for a CTA/V. All examinations were performed on a 16-section multidetector CT. The carotid bifurcations, internal carotid artery course, transverse and sigmoid sinuses, jugular foramen, internal jugular vein, sella turcica, and temporal bones were evaluated.
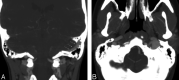
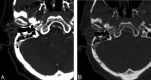
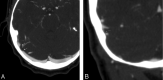
Results: Seven of the 16 patients had lesions on CTA/V that could account for their PT. Examples of pathologic conditions in the series included a significantly dominant venous system, a venous diverticulum with stricture, and a transverse sinus stenosis.
Conclusions: Preliminary findings indicate that CTA/V can be a valuable imaging tool in the assessment of PT. With this technique, arterial, venous, middle, and inner ear causes of PT can be excluded.
Figures
References
-
- Schleuning AJ 2nd. Management of the patient with tinnitus. Med Clin North Am 1991;75:1225–37 - PubMed
-
- Weissman JL, Hirsch BE. Imaging of tinnitus: A review. Radiology 2000;216:342–49 - PubMed
-
- Sismanis A. Pulsatile tinnitus. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 2003;36:389–402 - PubMed
-
- Lockwood AH, Salvi RJ, Burkard RF. Tinnitus. N Engl J Med 2002;347:904–10 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
