Expression of IL-1beta in supraspinal brain regions in rats with neuropathic pain
- PMID: 16973269
- PMCID: PMC1851944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.08.034
Expression of IL-1beta in supraspinal brain regions in rats with neuropathic pain
Abstract
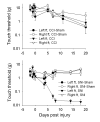
We examined mRNA expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1beta in the brainstem, thalamus, and prefrontal cortex in two rat models of neuropathic pain. Rats received a neuropathic injury: spared nerve injury (SNI) or chronic constriction injury (CCI), sham injury, or were minimally handled (control). Neuropathic pain-like behavior was monitored by tracking tactile thresholds. SNI-injured animals showed a robust decrease in tactile thresholds of the injured foot, while CCI-injured animals did not show tactile threshold changes. Ten or 24 days after nerve injury, IL-1beta gene expression in the brain was determined by RT-PCR. IL-1beta expression changes were observed mainly at 10 days after injury in the SNI animals, contralateral to the injury side, with increased expression in the brainstem and prefrontal cortex. The results indicate that neuro-immune activation in neuropathic pain conditions includes supraspinal brain regions, suggesting cytokine modulation of supraspinal circuitry of pain in neuropathic conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic neuropathic pain-like behavior correlates with IL-1β expression and disrupts cytokine interactions in the hippocampus.Pain. 2011 Dec;152(12):2827-2835. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.09.013. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Pain. 2011. PMID: 22033365 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a distinct neuro-immune signature in rats that develop behavioural disability after nerve injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 May 20;12:96. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0318-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25986444 Free PMC article.
-
Betamethasone affects cerebral expressions of NF-kappaB and cytokines that correlate with pain behavior in a rat model of neuropathy.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2006 Winter;36(1):39-46. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2006. PMID: 16501235
-
Chronic neuropathic pain-like behavior and brain-borne IL-1β.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Jul;1262(1):101-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06621.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22823441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nociceptive behavior in animal models for peripheral neuropathy: spinal and supraspinal mechanisms.Prog Neurobiol. 2008 Sep;86(1):22-47. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.06.002. Epub 2008 Jun 18. Prog Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18602968 Review.
Cited by
-
Ningmitai capsules have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects in the chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome mouse model through systemic immunity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 3;13:949316. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.949316. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36263126 Free PMC article.
-
Altered basal ganglia infraslow oscillation and resting functional connectivity in complex regional pain syndrome.J Neurosci Res. 2022 Jul;100(7):1487-1505. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25057. Epub 2022 Apr 20. J Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 35441738 Free PMC article.
-
Comorbidity Factors and Brain Mechanisms Linking Chronic Stress and Systemic Illness.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:5460732. doi: 10.1155/2016/5460732. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26977323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroplasticity of ascending and descending pathways after somatosensory system injury: reviewing knowledge to identify neuropathic pain therapeutic targets.Spinal Cord. 2016 May;54(5):330-40. doi: 10.1038/sc.2015.225. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Spinal Cord. 2016. PMID: 26754470 Review.
-
Impact of Exercise on Tramadol-Conditioned Place Preference.Brain Sci. 2025 Jan 18;15(1):89. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15010089. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 39851456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ledeboer A, Sloane EM, Milligan ED, Frank MG, Mahony JH, Maier SF, Watkins LR. Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat models of pain facilitation. Pain. 2005;115:71–83. - PubMed
-
- Wieseler-Frank J, Maier SF, Watkins LR. Glial activation and pathological pain. Neurochem. Int. 2004;45:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Zelenka M, Schafers M, Sommer C. Intraneural injection of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha into rat sciatic nerve at physiological doses induces signs of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2005;116:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi M, Dib B, Panerai AE. Interleukin-1 and nociception in the rat. J Neurosci. Res. 1998;53:645–650. - PubMed
-
- Oka T, Aou S, Hori T. Intracerebroventricular injection of interleukin-1 beta induces hyperalgesia in rats. Brain Res. 1993;624:61–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

