Human replication protein A unfolds telomeric G-quadruplexes
- PMID: 16973897
- PMCID: PMC1635258
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl564
Human replication protein A unfolds telomeric G-quadruplexes
Abstract
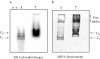
G-quadruplex structures inhibit telomerase activity and must be disrupted for telomere elongation during S phase. It has been suggested that the replication protein A (RPA) could unwind and maintain single-stranded DNA in a state amenable to the binding of telomeric components. We show here that under near-physiological in vitro conditions, human RPA is able to bind and unfold G-quadruplex structures formed from a 21mer human telomeric sequence. Analyses by native gel electrophoresis, cross-linking and fluorescence resonance energy transfer indicate the formation of both 1:1 and 2:1 complexes in which G-quadruplexes are unfolded. In addition, quadruplex opening by hRPA is much faster than observed with the complementary DNA, demonstrating that this protein efficiently unfolds G-quartets. A two-step mechanism accounting for the binding of hRPA to G-quadruplexes is proposed. These data point to the involvement of hRPA in regulation of telomere maintenance.
Figures
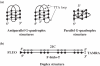

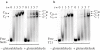
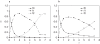


References
-
- Blackburn E.H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991;350:569–573. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn E.H. Telomere states and cell fates. Nature. 2000;408:53–56. - PubMed
-
- Li B., Oestreich S., de Lange T. Identification of human Rap1: implications for telomere evolution. Cell. 2000;101:471–483. - PubMed
-
- van Steensel B., Smogorzewska A., de Lange T. TRF2 protects human telomeres from end-to-end fusions. Cell. 1998;92:401–413. - PubMed
-
- Price C.M., Cech T.R. Telomeric DNA–protein interactions of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Genes Dev. 1987;1:783–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

