Hematologic manifestations of celiac disease
- PMID: 16973955
- PMCID: PMC1785098
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-031104
Hematologic manifestations of celiac disease
Abstract
Celiac disease is a common systemic disorder that can have multiple hematologic manifestations. Patients with celiac disease may present to hematologists for evaluation of various hematologic problems prior to receiving a diagnosis of celiac disease. Anemia secondary to malabsorption of iron, folic acid, and/or vitamin B12 is a common complication of celiac disease and many patients have anemia at the time of diagnosis. Celiac disease may also be associated with thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, venous thromboembolism, hyposplenism, and IgA deficiency. Patients with celiac disease are at increased risk of being diagnosed with lymphoma, especially of the T-cell type. The risk is highest for enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma (ETL) and B-cell lymphoma of the gut, but extraintestinal lymphomas can also be seen. ETL is an aggressive disease with poor prognosis, but strict adherence to a gluten-free diet may prevent its occurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: the authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
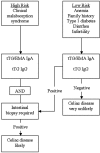
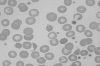
References
-
- Green PH, Jabri B. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 2003;362:383–391. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas ME, Krause PK, Gibson LE, Murray JA. Dermatitis herpetiformis. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:588–600. - PubMed
-
- Maki M, Mustalahti K, Kokkonen J, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease among children in Finland. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2517–2524. - PubMed
-
- Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:286–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

