Disulfiram effects on responses to intravenous cocaine administration
- PMID: 16979847
- PMCID: PMC1868516
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.08.016
Disulfiram effects on responses to intravenous cocaine administration
Abstract
Disulfiram has been studied as a treatment for cocaine dependence. We report results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, within-subject study to examine the interaction of disulfiram with intravenous cocaine.
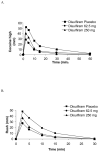
Methods: Non-treatment-seeking, cocaine-dependent, volunteers participated in serial experiments in which they received disulfiram placebo, 62.5 or 250 mg/day on days 1-6. On days 4-6, participants received a morning disulfiram dose 2 h prior to a scheduled session in which they were administered intravenous cocaine placebo, 0.25 mg/kg (n=9) or 0.5 mg/kg (n=3) over 1 min. Blood, cardiovascular and subjective measures were collected. Seven days of washout occurred between disulfiram conditions.
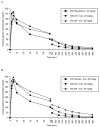
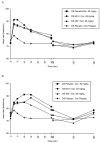
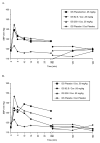
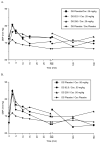
Results: Following active disulfiram treatments and cocaine 0.25 mg/kg administration, plasma cocaine AUC (0-480 min) was increased (p=0.003 and 0.001) and cocaine clearance decreased (p<0.001). Disulfiram treatments also decreased cocaine clearance for the 0.5 mg/kg cocaine dose (p=0.002 and<0.001). Neither disulfiram dose with cocaine altered cardiovascular responses relative to cocaine alone. Following cocaine 0.25 mg/kg, 'any high' (p=0.021 and 0.019), 'cocaine high' (p=0.017 and 0.018) and 'rush' (p=0.013 and 0.047) significantly decreased with either disulfiram dose.
Conclusions: Disulfiram decreased cocaine clearance without toxicity. Cocaine 'high' and 'rush' were diminished. Disulfiram may be a promising pharmacotherapy in selected cocaine dependent individuals.
Figures
References
-
- Beck O, Borg S, Holmstedt B, Kvande H, Shroder R. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol. Vol. 47. Copenh: 1980. Concentration of serotonin metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid from alcoholics before and during disulfiram therapy; pp. 305–307. - PubMed
-
- Beck O, Eriksson CJ, Kiianmaa K, Lundman A. 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid and 5-hydroxytryptophol levels in rat brain: effects of ethanol, pyrazole, cyanamide and disulfiram treatment. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1986;16:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Beck O, Helander A, Carlsson S, Borg S. Changes in serotonin metabolism during treatment with the aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors disulfiram and cyanamide. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1995;77:323–326. - PubMed
-
- Brien JF, Loomis CW. Disposition and pharmacokinetics of disulfiram and calcium carbimide (calcium cyanamide) Drug Metab Rev. 1983;14:113–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

