The large isoform of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin protein 2 plays a critical role in gene silencing and chromosome structure
- PMID: 16980400
- PMCID: PMC1667101
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.057604
The large isoform of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin protein 2 plays a critical role in gene silencing and chromosome structure
Abstract
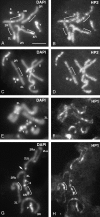
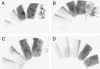
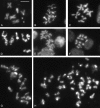
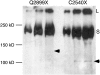
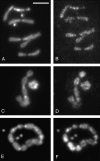
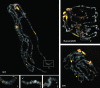
Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin protein 2 (HP2) interacts with heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1). In polytene chromosomes, HP2 and HP1 colocalize at the chromocenter, telomeres, and the small fourth chromosome. We show here that HP2 is present in the arms as well as the centromeric regions of mitotic chromosomes. We also demonstrate that Su(var)2-HP2 exhibits a dosage-dependent modification of variegation of a yellow reporter transgene, indicating a structural role in heterochromatin formation. We have isolated and characterized 14 new mutations in the Su(var)2-HP2 gene. Using wm4h, many (but not all) mutant alleles show dominant Su(var) activity. Su(var)2-HP2 mutant larvae show a wide variety of mitotic abnormalities, but not the telomere fusion seen in larvae deficient for HP1. The Su(var)2-HP2 gene codes for two isoforms: HP2-L (approximately 365 kDa) and HP2-S (approximately 175 kDa), lacking exons 5 and 6. In general, mutations that affect only the larger isoform result in more pronounced defects than do mutations common to both isoforms. This suggests that an imbalance between large and small isoforms is particularly deleterious. These results indicate a role for HP2 in the structural organization of chromosomes and in heterochromatin-induced gene silencing and show that the larger isoform plays a critical role in these processes.
Figures
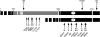


Similar articles
-
Heterochromatin protein 2 (HP2), a partner of HP1 in Drosophila heterochromatin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14332-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.212458899. Epub 2002 Oct 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12376620 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of heterochromatin protein 2 with HP1 defines a novel HP1-binding domain.Biochemistry. 2005 Oct 11;44(40):13394-403. doi: 10.1021/bi051006+. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16201764 Free PMC article.
-
The SU(VAR)3-9/HP1 complex differentially regulates the compaction state and degree of underreplication of X chromosome pericentric heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2007 Feb;175(2):609-20. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.062133. Epub 2006 Dec 6. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17151257 Free PMC article.
-
SU(VAR)3-9 is a conserved key function in heterochromatic gene silencing.Genetica. 2003 Mar;117(2-3):149-58. doi: 10.1023/a:1022923508198. Genetica. 2003. PMID: 12723694 Review.
-
Histone modification and the control of heterochromatic gene silencing in Drosophila.Chromosome Res. 2006;14(4):377-92. doi: 10.1007/s10577-006-1066-1. Chromosome Res. 2006. PMID: 16821134 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalent Fast Evolution of Genes Involved in Heterochromatin Functions.Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Sep 4;41(9):msae181. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae181. Mol Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39189646 Free PMC article.
-
The composition and organization of Drosophila heterochromatin are heterogeneous and dynamic.Elife. 2016 Aug 11;5:e16096. doi: 10.7554/eLife.16096. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27514026 Free PMC article.
-
A Distinct type of heterochromatin within Drosophila melanogaster chromosome 4.Genetics. 2007 Mar;175(3):1539-42. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.066407. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17194780 Free PMC article.
-
NBS1 interacts with HP1 to ensure genome integrity.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Dec 13;10(12):951. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2185-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31836699 Free PMC article.
-
In praise of mealybugs.J Genet. 2018 Jun;97(2):379-389. J Genet. 2018. PMID: 29932057 Review.
References
-
- Bannister, A. J., P. Zegerman, J. F. Partridge, E. A. Miska, J. O. Thomas et al., 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124. - PubMed
-
- Blom, N., S. Gammeltoft and S. Brunak, 1999. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J. Mol. Biol. 294: 1351–1362. - PubMed
-
- Cenci, G., G. Siriaco, G. D. Raffa, R. Kellum and M. Gatti, 2003. The Drosophila HOAP protein is required for telomere capping. Nat. Cell Biol. 5: 82–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

