Crl facilitates RNA polymerase holoenzyme formation
- PMID: 16980472
- PMCID: PMC1636326
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01266-06
Crl facilitates RNA polymerase holoenzyme formation
Abstract
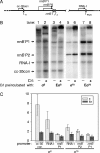
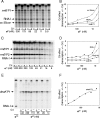
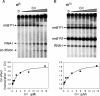
The Escherichia coli Crl protein has been described as a transcriptional coactivator for the stationary-phase sigma factor sigma(S). In a transcription system with highly purified components, we demonstrate that Crl affects transcription not only by the Esigma(S) RNA polymerase holoenzyme but also by Esigma(70) and Esigma(32). Crl increased transcription dramatically but only when the sigma concentration was low and when Crl was added to sigma prior to assembly with the core enzyme. Our results suggest that Crl facilitates holoenzyme formation, the first positive regulator identified with this mechanism of action.
Figures
References
-
- Arnqvist, A., A. Olsen, J. Pfeifer, D. G. Russell, and S. Normark. 1992. The Crl protein activates cryptic genes for curli formation and fibronectin binding in Escherichia coli HB101. Mol. Microbiol. 6:2443-2452. - PubMed
-
- Barker, M. M., T. Gaal, and R. L. Gourse. 2001. Mechanism of regulation of transcription initiation by ppGpp. II. Models for positive control based on properties of RNAP mutants and competition for RNAP. J. Mol. Biol. 305:689-702. - PubMed
-
- Barker, M. M., T. Gaal, C. A. Josaitis, and R. L. Gourse. 2001. Mechanism of regulation of transcription initiation by ppGpp. I. Effects of ppGpp on transcription initiation in vivo and in vitro. J. Mol. Biol. 305:673-688. - PubMed
-
- Bernardo, L., L. Johansson, D. Solera, E. Skärfstad, and V. Shingler. 2006. The guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) alarmone, DksA and promoter affinity for RNA polymerase in regulation of σ54-dependent transcription. Mol. Microbiol. 60:749-764. - PubMed
-
- Bougdour, A., C. Lelong, and J. Geiselmann. 2004. Crl, a low temperature-induced protein in Escherichia coli that binds directly to the stationary phase sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 279:19540-19550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

