Lipoprotein PssN of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii: subcellular localization and possible involvement in exopolysaccharide export
- PMID: 16980497
- PMCID: PMC1595502
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00651-06
Lipoprotein PssN of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii: subcellular localization and possible involvement in exopolysaccharide export
Abstract
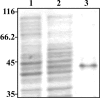
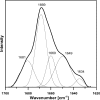
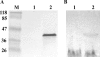
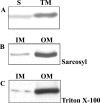
Surface expression of exopolysaccharides (EPS) in gram-negative bacteria depends on the activity of proteins found in the cytoplasmic membrane, the periplasmic space, and the outer membrane. pssTNOP genes identified in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii strain TA1 encode proteins that might be components of the EPS polymerization and secretion system. In this study, we have characterized PssN protein. Employing pssN-phoA and pssN-lacZ gene fusions and in vivo acylation with [3H]palmitate, we demonstrated that PssN is a 43-kDa lipoprotein directed to the periplasm by an N-terminal signal sequence. Membrane detergent fractionation followed by sucrose gradient centrifugation showed that PssN is an outer membrane-associated protein. Indirect immunofluorescence with anti-PssN and fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated antibodies and protease digestion of spheroplasts and intact cells of TA1 provided evidence that PssN is oriented towards the periplasmic space. Chemical cross-linking of TA1 and E. coli cells overproducing PssN-His6 protein showed that PssN might exist as a homo-oligomer of at least two monomers. Investigation of the secondary structure of purified PssN-His6 protein by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy revealed the predominant presence of beta-structure; however, alpha-helices were also detected. Influence of an increased amount of PssN protein on the TA1 phenotype was assessed and correlated with a moderate enhancement of EPS production.
Figures







Similar articles
-
PssO, a unique extracellular protein important for exopolysaccharide synthesis in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii.Biochimie. 2008 Nov-Dec;90(11-12):1781-90. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.08.004. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Biochimie. 2008. PMID: 18835420
-
Isolation and sequencing of Rhizobium leguminosarum Bv. Trifolii PssN, PssO and PssP genes encoding the proteins involved in polymerization and translocation of exopolysaccharide.DNA Seq. 2001 Jul;12(1):1-12. doi: 10.3109/10425170109042046. DNA Seq. 2001. PMID: 11697141
-
Homo- and heterotypic interactions between Pss proteins involved in the exopolysaccharide transport system in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii.Biol Chem. 2013 Apr;394(4):541-59. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0161. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23241669
-
Topological and transcriptional analysis of pssL gene product: a putative Wzx-like exopolysaccharide translocase in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii TA1.Arch Microbiol. 2005 Oct;184(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00203-005-0018-z. Epub 2005 Nov 3. Arch Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16044265
-
[Mycoplasmal membrane-bound lipoproteins capable of activating macrophages or fibroblasts to induce cytokine production].Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2000 Jan;55(1):11-20. doi: 10.3412/jsb.55.11. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 10695344 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Rhizobial Exopolysaccharides: Genetic Regulation of Their Synthesis and Relevance in Symbiosis with Legumes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 9;22(12):6233. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126233. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of Rhizobial Exopolysaccharides and Their Importance for Symbiosis with Legume Plants.Genes (Basel). 2017 Dec 1;8(12):360. doi: 10.3390/genes8120360. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29194398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental signals and regulatory pathways that influence exopolysaccharide production in rhizobia.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(11):7898-933. doi: 10.3390/ijms12117898. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22174640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii rosR is required for interaction with clover, biofilm formation and adaptation to the environment.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Nov 11;10:284. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-284. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21070666 Free PMC article.
-
PssJ Is a Terminal Galactosyltransferase Involved in the Assembly of the Exopolysaccharide Subunit in Rhizobium Leguminosarum bv. Trifolii.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 20;21(20):7764. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207764. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33092221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker, A., and A. Pühler. 1998. Production of exopolysaccharides, p. 97-118. In H. P. Spaink, A. Kondorosi, and P. J. J. Hooykaas (ed.), Rhizobiaceae. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
-
- Beringer, J. E., N. Brewin, A. W. Johnston, H. M. Schulman, and D. A. Hopwood. 1979. The Rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 204:219-233. - PubMed
-
- Bhasin, M., A. Garg, and G. P. S. Raghava. 2005. PSLpred: prediction of subcellular localization of bacterial proteins. Bioinformatics 21:2522-2524. - PubMed
-
- Bliss, J. M., and R. P. Silver. 1996. Coating the surface: a model for expression of capsular polysialic acid in Escherichia coli K1. Mol. Microbiol. 21:221-231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

