Dual role of the PhoP approximately P response regulator: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB45 phytase gene transcription is directed by positive and negative interactions with the phyC promoter
- PMID: 16980498
- PMCID: PMC1595534
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00681-06
Dual role of the PhoP approximately P response regulator: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB45 phytase gene transcription is directed by positive and negative interactions with the phyC promoter
Abstract
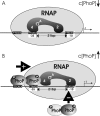
Several Bacillus strains secrete phytase, an enzyme catalyzing dephosphorylation of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate (phytate). We identified the phyC (phytase) gene from environmental Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB45 as a member of the phosphate starvation-inducible PhoPR regulon. In vivo and in vitro assays revealed that PhoP approximately P is essential for phyC transcription. The transcriptional start site was identified downstream of a sigmaA-like promoter region located 27 bp upstream of the probable translation ATG start codon. Inspection of the phyC promoter sequence revealed an unusual structure. The -35 and -10 regions are separated by a window of 21 bp. A pair of tandemly repeated PhoP TT(T/A/C)ACA binding boxes was located within and upstream of the -35 consensus promoter region. A single PhoP box was found within the -10 consensus promoter region. DNase I footprinting experiments performed with isolated PhoP confirmed that PhoP approximately P binds at two sites overlapping with the phyC -35 and -10 consensus promoter region. While binding of dimeric PhoP approximately P at -35 is essential for activation of the phyC promoter, binding of PhoP approximately P at -10 suppresses promoter activity. A sixfold enhancement of phyC gene expression was registered after T:G substitution of nucleotide -13 (mutant MUT13), which eliminates PhoP binding at the single PhoP box without impairing the -10 consensus sequence. Moreover, MUT13 also expressed phyC during phosphate-replete growth, suggesting that the repressing effect due to binding of PhoP approximately P at -10 was abolished. A model is presented in which transcription initiation of phyC is positively and negatively affected by the actual concentration of the PhoP approximately P response regulator.
Figures
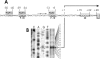

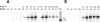
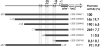
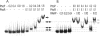


Similar articles
-
Thermodynamic and molecular analysis of the AbrB-binding sites within the phyC-region of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB45.Mol Genet Genomics. 2012 Feb;287(2):111-22. doi: 10.1007/s00438-011-0666-4. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Mol Genet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22183144
-
Transition state regulator AbrB inhibits transcription of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB45 phytase through binding at two distinct sites located within the extended phyC promoter region.J Bacteriol. 2008 Oct;190(19):6467-74. doi: 10.1128/JB.00430-08. Epub 2008 Aug 1. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18676675 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of PhoP binding to the tuaA promoter with PhoP binding to other Pho-regulon promoters establishes a Bacillus subtilis Pho core binding site.Microbiology (Reading). 1998 May;144 ( Pt 5):1443-1450. doi: 10.1099/00221287-144-5-1443. Microbiology (Reading). 1998. PMID: 9611818
-
Mutational analysis of the phoD promoter in Bacillus subtilis: implications for PhoP binding and promoter activation of Pho regulon promoters.J Bacteriol. 1999 Apr;181(7):2017-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.7.2017-2025.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10094677 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphate control of phoA, phoC and phoD gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor reveals significant differences in binding of PhoP to their promoter regions.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Oct;153(Pt 10):3527-3537. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/007070-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17906150
Cited by
-
Enhanced Expression of Pullulanase in Bacillus subtilis by New Strong Promoters Mined From Transcriptome Data, Both Alone and in Combination.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 2;9:2635. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02635. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30450090 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing and assessment of plant growth-promoting properties of a Serratia marcescens strain isolated from vermicompost.BMC Genomics. 2018 Oct 16;19(1):750. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5130-y. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30326830 Free PMC article.
-
Differential proteomic analysis highlights metabolic strategies associated with balhimycin production in Amycolatopsis balhimycina chemostat cultivations.Microb Cell Fact. 2010 Nov 26;9:95. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-9-95. Microb Cell Fact. 2010. PMID: 21110849 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamic and molecular analysis of the AbrB-binding sites within the phyC-region of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB45.Mol Genet Genomics. 2012 Feb;287(2):111-22. doi: 10.1007/s00438-011-0666-4. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Mol Genet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22183144
-
Rhizopine biosensors for plant-dependent control of bacterial gene expression.Environ Microbiol. 2023 Feb;25(2):383-396. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.16288. Epub 2022 Dec 4. Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36428208 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

