Whole-genome transcriptional analysis of chemolithoautotrophic thiosulfate oxidation by Thiobacillus denitrificans under aerobic versus denitrifying conditions
- PMID: 16980503
- PMCID: PMC1595532
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00568-06
Whole-genome transcriptional analysis of chemolithoautotrophic thiosulfate oxidation by Thiobacillus denitrificans under aerobic versus denitrifying conditions
Abstract
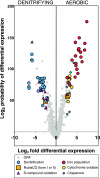
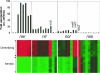
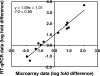
Thiobacillus denitrificans is one of the few known obligate chemolithoautotrophic bacteria capable of energetically coupling thiosulfate oxidation to denitrification as well as aerobic respiration. As very little is known about the differential expression of genes associated with key chemolithoautotrophic functions (such as sulfur compound oxidation and CO2 fixation) under aerobic versus denitrifying conditions, we conducted whole-genome, cDNA microarray studies to explore this topic systematically. The microarrays identified 277 genes (approximately 10% of the genome) as differentially expressed using RMA (robust multiarray average) statistical analysis and a twofold cutoff. Genes upregulated (ca. 6- to 150-fold) under aerobic conditions included a cluster of genes associated with iron acquisition (e.g., siderophore-related genes), a cluster of cytochrome cbb3 oxidase genes, cbbL and cbbS (encoding the large and small subunits of form I ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, or RubisCO), and multiple molecular chaperone genes. Genes upregulated (ca. 4- to 95-fold) under denitrifying conditions included nar, nir, and nor genes (associated, respectively, with nitrate reductase, nitrite reductase, and nitric oxide reductase, which catalyze successive steps of denitrification), cbbM (encoding form II RubisCO), and genes involved with sulfur compound oxidation (including two physically separated but highly similar copies of sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase and of dsrC, associated with dissimilatory sulfite reductase). Among genes associated with denitrification, relative expression levels (i.e., degree of upregulation with nitrate) tended to decrease in the order nar > nir > nor > nos. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR analysis was used to validate these trends.
Figures


References
-
- Andrews, S. C., A. K. Robinson, and F. Rodriguez-Quiñones. 2003. Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27:215-237. - PubMed
-
- Arai, H., M. Mizutani, and Y. Igarashi. 2003. Transcriptional regulation of the nos genes for nitrous oxide reductase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology (United Kingdom) 149:29-36. - PubMed
-
- Beller, H. R., P. S. G. Chain, T. E. Letain, A. Chakicherla, F. W. Larimer, P. M. Richardson, M. A. Coleman, A. P. Wood, and D. P. Kelly. 2006. The genome sequence of the obligately chemolithoautotrophic, facultatively anaerobic bacterium Thiobacillus denitrificans. J. Bacteriol. 188:1473-1488. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

