Tid1/Rdh54 promotes dissociation of Dmc1 from nonrecombinogenic sites on meiotic chromatin
- PMID: 16980587
- PMCID: PMC1578681
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1447106
Tid1/Rdh54 promotes dissociation of Dmc1 from nonrecombinogenic sites on meiotic chromatin
Abstract
The meiosis-specific recombinase Dmc1 plays a critical role in DNA strand exchange in budding yeast. Tid1/Rdh54, a member of the Swi2/Snf2 family of DNA translocases, has been shown to stimulate Dmc1-dependent recombination. Tid1and its budding yeast paralog Rad54 have a variety of biochemical activities that may contribute to their biological function. Here we demonstrate that Dmc1 can associate with chromatin in the absence of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), and Tid1 suppresses this association. Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments indicate that an activity shared by Tid1 and Rad54 is required for normal assembly of Dmc1 at DSB sites in preparation for recombination. These results lead to a model in which the ATP hydrolysis-dependent DNA translocase activity of Tid1 acts to promote dissociation of Dmc1 from nonreombinogenic sites on chromatin, with Rad54 being able to substitute for this function in the absence of Tid1. The tendency of Dmc1 to form unproductive interactions with chromatin is proposed to be a consequence of the mechanism of strand exchange. The results raise the possibility that ATP hydrolysis-dependent disruption of nonproductive recombinase-DNA interactions is a feature shared with other homologous recombination systems.
Figures


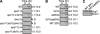
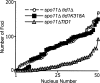
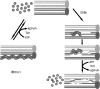
Comment in
-
Some disassembly required: role of DNA translocases in the disruption of recombination intermediates and dead-end complexes.Genes Dev. 2006 Sep 15;20(18):2479-86. doi: 10.1101/gad.1477106. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16980577 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dmc1 and Rad51 proteins preferentially function with Tid1 and Rad54 proteins, respectively, to promote DNA strand invasion during genetic recombination.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28727-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.373290. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22761450 Free PMC article.
-
Tid1/Rdh54 promotes colocalization of rad51 and dmc1 during meiotic recombination.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Sep 26;97(20):10814-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.20.10814. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11005857 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the roles of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD54 gene and a homologue of RAD54, RDH54/TID1, in mitosis and meiosis.Genetics. 1997 Dec;147(4):1545-56. doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.4.1545. Genetics. 1997. PMID: 9409820 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of the Snf2/Swi2 family Rad54 motor protein in homologous recombination.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Sep;1809(9):509-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.06.006. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21704205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombination proteins in yeast.Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:233-71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.091500. Annu Rev Genet. 2004. PMID: 15568977 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of recombination and genomic maintenance.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Aug 3;7(8):a016501. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016501. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26238353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Dissection of Vps13 Regulation in Yeast Using Disease Mutations from Human Orthologs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 8;22(12):6200. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126200. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201352 Free PMC article.
-
Rad51 and Rad54 ATPase activities are both required to modulate Rad51-dsDNA filament dynamics.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):4124-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm412. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17567608 Free PMC article.
-
RAD54 controls access to the invading 3'-OH end after RAD51-mediated DNA strand invasion in homologous recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Feb;37(2):638-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn980. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19074197 Free PMC article.
-
Rad54 and Rdh54 occupy spatially and functionally distinct sites within the Rad51-ssDNA presynaptic complex.EMBO J. 2020 Oct 15;39(20):e105705. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105705. Epub 2020 Aug 13. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32790929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexeev, A., Mazin, A., Kowalczykowski, S.C. Rad54 protein possesses chromatin-remodeling activity stimulated by the Rad51–ssDNA nucleoprotein filament. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003;10:182–186. - PubMed
-
- Amitani, I., Baskin, R.J., Kowalczykowski, S.C. Visualization of Rad54, a chromatin remodeling protein, translocating on single DNA molecules. Mol. Cell. 2006;23:143–148. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, D.K. RecA homologs Dmc1 and Rad51 interact to form multiple nuclear complexes prior to meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1994;79:1081–1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
