Modulation of a P-TEFb functional equilibrium for the global control of cell growth and differentiation
- PMID: 16980611
- PMCID: PMC1592901
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00778-06
Modulation of a P-TEFb functional equilibrium for the global control of cell growth and differentiation
Abstract
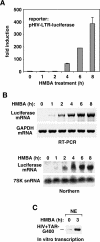
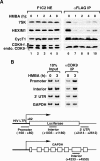
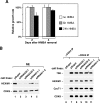
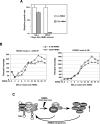
P-TEFb phosphorylates RNA polymerase II and negative elongation factors to stimulate general transcriptional elongation. It is kept in a functional equilibrium through alternately interacting with its positive (the Brd4 protein) and negative (the HEXIM1 protein and 7SK snRNA) regulators. To investigate the physiological significance of this phenomenon, we analyzed the responses of HeLa cells and murine erythroleukemia cells (MELC) to hexamethylene bisacetamide (HMBA), which inhibits growth and induces differentiation of many cell types. For both cell types, an efficient, albeit temporary disruption of the 7SK-HEXIM1-P-TEFb snRNP and enhanced formation of the Brd4-P-TEFb complex occurred soon after the treatment started. When the P-TEFb-dependent HEXIM1 expression markedly increased as the treatment continued, the abundant HEXIM1 pushed the P-TEFb equilibrium back toward the 7SK/HEXIM1-bound state. For HeLa cells, as HMBA produced only a minor, temporary effect on their growth, the equilibrium gradually returned to its pretreatment level. In contrast, long-term treatment of MELC induced terminal division and differentiation. Concurrently, the P-TEFb equilibrium was shifted overwhelmingly toward the 7SK snRNP side. Together, these data link the P-TEFb equilibrium to the intracellular transcriptional demand and proliferative/differentiated states of cells.
Figures


References
-
- Bellan, C., G. De Falco, S. Lazzi, P. Micheli, S. Vicidomini, K. Schurfeld, T. Amato, A. Palumbo, L. Bagella, E. Sabattini, S. Bartolommei, M. Hummel, S. Pileri, P. Tosi, L. Leoncini, and A. Giordano. 2004. CDK9/CYCLIN T1 expression during normal lymphoid differentiation and malignant transformation. J. Pathol. 203:946-952. - PubMed
-
- Byers, S. A., J. P. Price, J. J. Cooper, Q. Li, and D. H. Price. 2005. HEXIM2, a HEXIM1-related protein, regulates positive transcription elongation factor b through association with 7SK. J. Biol. Chem. 280:16360-16367. - PubMed
-
- Chao, S.-H., and D. H. Price. 2001. Flavopiridol inactivates P-TEFb and blocks most RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 276:31793-31799. - PubMed
-
- Chen, R., Z. Yang, and Q. Zhou. 2004. Phosphorylated positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) is tagged for inhibition through association with 7SK snRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 279:4153-4160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
