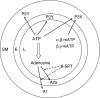
Regional vascular responses to ATP and ATP analogues in the rabbit kidney in vivo: roles for adenosine receptors and prostanoids
- PMID: 16981003
- PMCID: PMC2014670
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706901
Regional vascular responses to ATP and ATP analogues in the rabbit kidney in vivo: roles for adenosine receptors and prostanoids
Abstract
Background and purpose: Our knowledge of the effects of P2-receptor activation on renal vascular tone comes mostly from in vitro models. We aimed to characterise the pharmacology of ATP in the renal circulation in vivo.
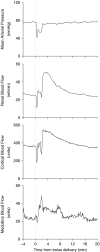
Experimental approach: In pentobarbitone anaesthetized rabbits, we examined total renal and medullary vascular responses to ATP (0.2 and 0.8 mg kg(-1)), beta, gamma-methylene ATP (beta, gamma-mATP, 7 and 170 microg kg(-1)), alpha, beta-mATP (0.2 and 2 microg kg(-1)) and adenosine (2 and 6 microg kg(-1)) using transit-time ultrasound and laser Doppler flowmetry, respectively. We also determined whether adenosine receptors, NO or prostanoids contribute to the actions of the purinoceptor agonists.
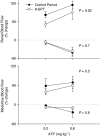
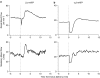
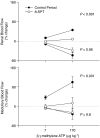
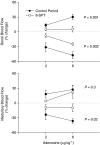
Key results: Renal arterial boluses of ATP, beta,gamma-mATP, and adenosine produced biphasic changes; ischaemia followed by hyperaemia, in total renal and medullary blood flow. alpha,beta-mATP induced only ischaemia. The adenosine receptor antagonist 8-(p-sulphophenyl)theophylline reduced the responses to adenosine and the hyperaemic responses to ATP and beta,gamma-mATP only. NO synthase inhibition (Nomega-nitro-L-arginine) did not significantly alter responses to the P2 receptor agonists. Subsequent cyclooxygenase inhibition (ibuprofen) reduced the ATP- and beta, gamma-mATP-induced increases in renal blood flow. All other responses remained unchanged.
Conclusions and implications: In the rabbit kidney in vivo, alpha, beta-mATP sensitive receptors mediate vasoconstriction. beta,gamma-mATP and ATP induce vasodilation at least partly through adenosine receptors. ATP induced renal vasodilatation is independent of NO and partly dependent on prostanoids in the bulk of the kidney, but not in the vasculature controlling medullary blood flow.
Figures



References
-
- Chan CM, Unwin RJ, Bardini M, Oglesby IB, Ford AP, Townsend-Nicholson A, et al. Localization of P2X1 purinoceptors by autoradiography and immunohistochemistry in rat kidneys. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1998;274:F799–F804. - PubMed
-
- Chen CC, Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Colquhoun D, Burnstock G, Wood JN. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature. 1995;377:428–431. - PubMed
-
- Daly JW, Padgett W, Shamim MT, Butts-Lamb P, Waters J. 1,3-Dialkyl-8-(p-sulfophenyl)xanthines: potent water-soluble antagonists for A1- and A2-adenosine receptors. J Med Chem. 1985;28:487–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

