Small molecules with antimicrobial activity against E. coli and P. aeruginosa identified by high-throughput screening
- PMID: 16981005
- PMCID: PMC2014677
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706873
Small molecules with antimicrobial activity against E. coli and P. aeruginosa identified by high-throughput screening
Abstract
Background and purpose: New antimicrobials are needed because of the emergence of organisms that are resistant to available antimicrobials. The purpose of this study was to evaluate a high-throughput screening approach to identify antibacterials against two common disease-causing bacteria, and to determine the frequency, novelty, and potency of compounds with antibacterial activity.
Experimental approach: A high-throughput, turbidometric assay of bacterial growth in a 96-well plate format was used to screen a diverse collection of 150,000 small molecules for antibacterial activity against E. coli and P. aeruginosa. The statistical Z'-factor for the assay was > or = 0.7.
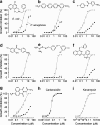
Key results: Screening for inhibition of E. coli growth gave a 'hit' rate (> 60% inhibition at 12.5 microM) of 0.025%, which was more than 5-fold reduced for P. aeruginosa. The most potent antibacterials (EC50 < 0.5 microM) were of the nitrofuran class followed by naphthalimide, salicylanilide, bipyridinium and quinoazolinediamine chemical classes. Screening of > 250 analogs of the most potent antibacterial classes established structure-activity data sets.
Conclusions and implications: Our results validate and demonstrate the utility of a growth-based phenotype screen for rapid identification of small-molecule antibacterials. The favourable efficacy and structure-activity data for several of the antibacterial classes suggests their potential development for clinical use.
Figures


References
-
- Alanis AJ. Resistance to antibiotics: are we in the post-antibiotic era. Arch Med Res. 2005;36:697–705. - PubMed
-
- Allsop AE. Bacterial genome sequencing and drug discovery. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1998;9:637–642. - PubMed
-
- Amegadzie AKC, Elizabeth M, Domagala JM, Huang L, Micetich RG, Singh R, et al. Preparation of isoquinolones as antibacterial agents PCT Int Appl 1998CodenPIXXD2,Patent no. WO9819648
-
- Anderson RT, Jr, Santi DV. Phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase from Escherichia coli B. Potent inhibition by analogs of N-benzyl-2-phenylethylamine. J Med Chem. 1976;19:1270–1275. - PubMed
-
- Awada A, Thoedtmann R, Piccart MJ, Wanders J, Schrijvers AHGJ, Von Broen I-M, et al. An EORTC-ECSG phase I study of LU 79553 administered every 21 or 42 days in patients with solid tumors. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:742–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL73856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK72517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059198/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- EY13574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK35124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EB00415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- HL59198/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

