Selective tyrosine kinase inhibition by imatinib mesylate for the treatment of autoimmune arthritis
- PMID: 16981009
- PMCID: PMC1564430
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI28546
Selective tyrosine kinase inhibition by imatinib mesylate for the treatment of autoimmune arthritis
Abstract
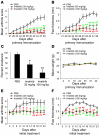
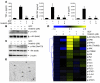
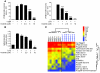
Tyrosine kinases play a central role in the activation of signal transduction pathways and cellular responses that mediate the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Imatinib mesylate (imatinib) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor developed to treat Bcr/Abl-expressing leukemias and subsequently found to treat c-Kit-expressing gastrointestinal stromal tumors. We demonstrate that imatinib potently prevents and treats murine collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). We further show that micromolar concentrations of imatinib abrogate multiple signal transduction pathways implicated in RA pathogenesis, including mast cell c-Kit signaling and TNF-alpha release, macrophage c-Fms activation and cytokine production, and fibroblast PDGFR signaling and proliferation. In our studies, imatinib attenuated PDGFR signaling in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) and TNF-alpha production in synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs) derived from human RA patients. Imatinib-mediated inhibition of a spectrum of signal transduction pathways and the downstream pathogenic cellular responses may provide a powerful approach to treat RA and other inflammatory diseases.
Figures


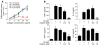
References
-
- Firestein G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Druker B.J., et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Demetri G.D., et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;347:472–480. - PubMed
-
- Buchdunger E., Matter A., Druker B.J. Bcr-Abl inhibition as a modality of CML therapeutics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2001;1551:M11–M18. - PubMed
-
- Dewar A.L., et al. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor c-fms is a novel target of imatinib. Blood. 2005;105:3127–3132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

