Would artificial neural networks implemented in clinical wards help nephrologists in predicting epoetin responsiveness?
- PMID: 16981983
- PMCID: PMC1578551
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-7-13
Would artificial neural networks implemented in clinical wards help nephrologists in predicting epoetin responsiveness?
Abstract
Background: Due to its strong intra- and inter-individual variability, predicting the ideal erythropoietin dose is a difficult task. The aim of this study was to re-evaluate the impact of the main parameters known to influence the responsiveness to epoetin beta and to test the performance of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in predicting the dose required to reach the haemoglobin target and the monthly dose adjustments.
Methods: We did a secondary analysis of the survey on Anaemia Management in dialysis patients in Switzerland; a prospective, non-randomized observational study, enrolling 340 patients of 26 centres and in order to have additional information about erythropoietin responsiveness, we included a further 92 patients from the Renal Services of the Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale, Bellinzona, Switzerland. The performance of ANNs in predicting the epoetin dose was compared with that of linear regressions and of nephrologists in charge of the patients.
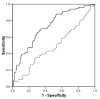
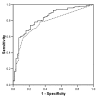
Results: For a specificity of 50%, the sensitivity of ANNs compared with linear regressions in predicting the erythropoietin dose to reach the haemoglobin target was 78 vs. 44% (P < 0.001). The ANN built to predict the monthly adaptations in erythropoietin dose, compared with the nephrologists' opinion, allowed to detect 48 vs. 25% (P < 0.05) of the patients treated with an insufficient dose with a specificity of 92 vs. 83% (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: In predicting the erythropoietin dose required for an individual patient and the monthly dose adjustments ANNs are superior to nephrologists' opinion. Thus, ANN may be a useful and promising tool that could be implemented in clinical wards to help nephrologists in prescribing erythropoietin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Predicting intradialytic hypotension from experience, statistical models and artificial neural networks.J Nephrol. 2005 Jul-Aug;18(4):409-16. J Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 16245245
-
Once-monthly subcutaneous C.E.R.A. maintains stable hemoglobin control in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis and converted directly from epoetin one to three times weekly.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Jul;2(4):637-46. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03631006. Epub 2007 May 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17699476 Clinical Trial.
-
Artificial neural networks improve the prediction of Kt/V, follow-up dietary protein intake and hypotension risk in haemodialysis patients.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004 May;19(5):1204-11. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfh084. Epub 2004 Feb 19. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004. PMID: 14993478
-
Development and exploitation of a clinical decision support system for the management of renal anaemia.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007 Jun;22 Suppl 4:iv31-iv36. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm163. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17526548 Review.
-
The latest advances in kidney diseases and related disorders.Drug News Perspect. 2007 May;20(4):271-8. Drug News Perspect. 2007. PMID: 17637941 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance of a Predictive Model for Long-Term Hemoglobin Response to Darbepoetin and Iron Administration in a Large Cohort of Hemodialysis Patients.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 3;11(3):e0148938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148938. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26939055 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting technique survival in peritoneal dialysis patients: comparing artificial neural networks and logistic regression.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008 Sep;23(9):2972-81. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn187. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18441002 Free PMC article.
-
Using Artificial Intelligence Resources in Dialysis and Kidney Transplant Patients: A Literature Review.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 10;2020:9867872. doi: 10.1155/2020/9867872. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32596403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Feedback Control Design in Developing Anemia Management Protocols.Ann Biomed Eng. 2021 Jan;49(1):171-179. doi: 10.1007/s10439-020-02520-1. Epub 2020 May 7. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 32383041 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Analysis of Time-Dependent Features for Predicting Adverse Events During Hemodialysis Therapy: Model Development and Validation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Sep 7;23(9):e27098. doi: 10.2196/27098. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34491204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NKF-K/DOQI Clinical practice guidelines for anemia of chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;37:S182–238. - PubMed
-
- Mayer G, Thum J, Cada EM, Stummvoll HK, Graf H. Working capacity is increased following recombinant human erythropoietin treatment. Kidney Int. 1988;34:525–528. - PubMed
-
- Bàràny P, Petterson E, Konarski-Svensson JK. Long-term effects on quality of life in haemodialysis patients of correction of anaemia with erythropoietin. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1993;8:426–432. - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Harnett JD, Kent GM, Murray DC, Barre PE. The impact of Anemia on Cardiomyopathy, Morbidity, and Mortality in End-Stage Renal Disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996;28:53–61. - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Aljama P, Bàràny P, Canaud B, Carrera F, Eckhardt KU, Hörl WH, Macdougall IC, Macleod A, Wiecek A, Cameron S. Revised European Best Practice Guidelines for the management of anaemia in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19 Suppl 2:ii1–47. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfh1032. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

