Kinetics of progenitor hemopoetic stem cells in sepsis: correlation with patients survival?
- PMID: 16981997
- PMCID: PMC1586204
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-142
Kinetics of progenitor hemopoetic stem cells in sepsis: correlation with patients survival?
Abstract
Background: Current theories underline the crucial role of pro-inflammatory mediators produced by monocytes for the pathogenesis of sepsis. Since monocytes derive from progenitor hemopoetic cells, the kinetics of stem cells was studied in peripheral blood of patients with sepsis.
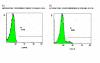
Methods: Blood was sampled from 44 patients with septic syndrome due to ventilator-associated pneumonia on days 1, 3, 5 and 7 upon initiation of symptoms. Concentrations of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8 and G-CSF were estimated by ELISA. CD34/CD45 cells were determined after incubation with anti-CD45 FITC and anti-CD34 PE monocloncal antibodies and flow cytometric analysis. Samples from eight healthy volunteers served as controls.
Results: Median of CD34/CD45 absolute count of controls was 1.0/mul. Respective values of the total study population were 123.4, 112.4, 121.5 and 120.9/mul on days 1, 3, 5 and 7 (p < 0.0001 compared to controls). Positive correlations were found between the absolute CD34/CD45 count and the absolute monocyte count on days 1, 5 and 7. Survival was prolonged among patients with less than 310/microl CD34/CD45 cells on day 1 compared to those with more than 310/microl of CD34/CD45 cells (p: 0.022). Hazard ratio for death due to sepsis was 5.47 (p: 0.039) for CD34/CD45 cells more than 310/microl. Median IL-6 on day 1 was 56.78 and 233.85 pg/ml respectively for patients with less than 310/microl and more than 310/microl CD34/CD45 cells (p: 0.021).
Conclusion: Stem cells are increased in peripheral blood over all days of follow-up compared to healthy volunteers. Patients with counts on day 1 less than 310/microl are accompanied by increased survival compared to patients with more than 310/microl.
Figures


References
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Osmon SB, Chang KC, Wagner TH, Coopersmith CM, Karl IE. Accelerated lymphocyte death in sepsis occurs by both the death receptor and mitochondrial pathways. J Clin Oncol. 2005;174:5110–5118. - PubMed
-
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Routsi C, Plachouras D, Markaki V, Raftogiannis M, Zervakis D, Koussoulas V, Orfanos S, Kotanidou A, Armaganidis A, Roussos C, Giamarellou H. Early apoptosis of blood monocytes in the septic host: is it a mechanism of protection in the event of septic shock? Crit Care. 2006;10:R76. doi: 10.1186/cc4921. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lynch L, O'Donoghue D, Dean J, O'Sullivan J, O'Farrelly C, Golden-Mason L. Detection and characterization of hemopoeitic stem cells in the adult human small intestine. J Immunol. 2006;176:5199–5204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

