NEIL2-initiated, APE-independent repair of oxidized bases in DNA: Evidence for a repair complex in human cells
- PMID: 16982218
- PMCID: PMC2805168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.07.003
NEIL2-initiated, APE-independent repair of oxidized bases in DNA: Evidence for a repair complex in human cells
Abstract
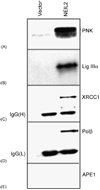
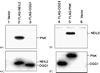
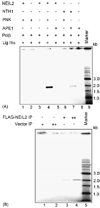
DNA glycosylases/AP lyases initiate repair of oxidized bases in the genomes of all organisms by excising these lesions and then cleaving the DNA strand at the resulting abasic (AP) sites and generate 3' phospho alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde (3' PUA) or 3' phosphate (3' P) terminus. In Escherichia coli, the AP-endonucleases (APEs) hydrolyze both 3' blocking groups (3' PUA and 3' P) to generate the 3'-OH termini needed for repair synthesis. In mammalian cells, the previously characterized DNA glycosylases, NTH1 and OGG1, produce 3' PUA, which is removed by the only AP-endonuclease, APE1. However, APE1 is barely active in removing 3' phosphate generated by the recently discovered mammalian DNA glycosylases NEIL1 and NEIL2. We showed earlier that the 3' phosphate generated by NEIL1 is efficiently removed by polynucleotide kinase (PNK) and not APE1. Here we show that the NEIL2-initiated repair of 5-hydroxyuracil (5-OHU) similarly requires PNK. We have also observed stable interaction between NEIL2 and other BER proteins DNA polymerase beta (Pol beta), DNA ligase IIIalpha (Lig IIIalpha) and XRCC1. In spite of their limited sequence homology, NEIL1 and NEIL2 interact with the same domains of Pol beta and Lig IIIalpha. Surprisingly, while the catalytically dispensable C-terminal region of NEIL1 is the common interacting domain, the essential N-terminal segment of NEIL2 is involved in analogous interaction. The BER proteins including NEIL2, PNK, Pol beta, Lig IIIalpha and XRCC1 (but not APE1) could be isolated as a complex from human cells, competent for repair of 5-OHU in plasmid DNA.
Figures


References
-
- Breimer LH. Molecular mechanisms of oxygen radical carcinogenesis and mutagenesis: the role of DNA base damage. Mol. Carcinog. 1990;3:188–197. - PubMed
-
- Shibutani S. Takeshita M. Grollman AP. Insertion of specific bases during DNA synthesis past the oxidation-damaged base 8-oxodG. Nature. 1991;349:431–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AG021830/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA92584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA102271/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES012512/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 ES050159/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES06676/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA81063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA092584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES012512/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102271/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES006676/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

