Spatial compartmentalization of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1-dependent signaling pathways in human airway smooth muscle cells. Lipid rafts are essential for TNF-alpha-mediated activation of RhoA but dispensable for the activation of the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways
- PMID: 16982613
- PMCID: PMC2653078
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M605738200
Spatial compartmentalization of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1-dependent signaling pathways in human airway smooth muscle cells. Lipid rafts are essential for TNF-alpha-mediated activation of RhoA but dispensable for the activation of the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways
Abstract
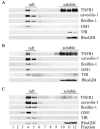
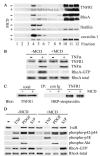
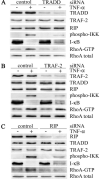
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-induced activation of RhoA, mediated by TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1), is a prerequisite step in a pathway that leads to increased 20-kDa light chain of myosin (MLC20) phosphorylation and airway smooth muscle contraction. In this study, we have investigated the proximal events in TNF-alpha-induced RhoA activation. TNFR1 is localized to both lipid raft and nonraft regions of the plasma membrane in primary human airway smooth muscle cells. TNF-alpha engagement of TNFR1 recruited the adaptor proteins TRADD, TRAF-2, and RIP into lipid rafts and activated RhoA, NF-kappaB, and MAPK pathways. Depletion of cholesterol from rafts with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin caused a redistribution of TNFR1 to nonraft plasma membrane and prevented ligand-induced RhoA activation. By contrast, TNF-alpha-induced activation of NF-kappaB and MAPKs was unaffected by methyl-beta-cyclodextrin indicating that, in airway smooth muscle cells, activation of these pathways occurred independently of lipid rafts. Targeted knockdown of caveolin-1 completely abrogated TNF-alpha-induced RhoA activation, identifying this raft-resident protein as a positive regulator of the activation process. The signaling adaptors TRADD and RIP were also found to be necessary for ligand-induced RhoA activation. Taken together, our results suggest that in airway smooth muscle cells, spatial compartmentalization of TNFR1 provides a mechanism for generating distinct signaling outcomes in response to ligand engagement and define a mechanistic role for lipid rafts and caveolin-1 in TNF-alpha-induced activation of RhoA.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and its signaling intermediates are recruited to lipid rafts in the traumatized brain.J Neurosci. 2004 Dec 8;24(49):11010-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3823-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15590916 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of TNF-R1 signaling: lipid raft dependency of p42mapk/erk2 activation, but not NF-kappaB activation.J Immunol. 2004 Jun 15;172(12):7654-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7654. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15187147
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) induces upregulation of RhoA via NF-kappaB activation in cultured human bronchial smooth muscle cells.J Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Aug;110(4):437-44. doi: 10.1254/jphs.09081fp. Epub 2009 Jul 14. J Pharmacol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19602845
-
The role of TRADD in death receptor signaling.Cell Cycle. 2012 Mar 1;11(5):871-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.5.19300. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22333735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26993379 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 represses c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated apoptosis via NF-kappaB regulation.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 25;283(30):21011-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802229200. Epub 2008 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18508759 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Blockade of TNFR1 Improves Clinical Disease and Bronchoconstriction in Experimental RSV Infection.Viruses. 2020 Oct 17;12(10):1176. doi: 10.3390/v12101176. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33080861 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated expression of microRNAs and mRNAs in pulmonary artery remodeling in ascites syndrome in broiler chickens.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):1993-2007. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12888. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27791988 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 knockout mice exhibit airway hyperreactivity.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):L669-81. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00018.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22923642 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF2 facilitates vaccinia virus replication by promoting rapid virus entry.J Virol. 2014 Apr;88(7):3664-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03013-13. Epub 2014 Jan 15. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24429366 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

